Aquaporin-1
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Aquaporin 1 (AQP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AQP1 gene.
AQP-1 is a widely expressed water channel, whose physiological function has been most thoroughly characterized in the kidney. It is found in the basolateral and apical plasma membranes of the proximal tubules, the descending limb of the loop of Henle, and in the descending portion of the vasa recta. Additionally, it is found in red blood cells, vascular endothelium, the gastrointestinal tract, sweat glands, lungs, and the central nervous system.[5]
Neural AQP-1 are regulated by vasopressin AVPR1A receptor activity.[6]
Function
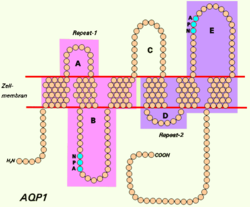
Aquaporins are a family of small integral membrane proteins related to the major intrinsic protein (MIP or AQP0). This gene encodes an aquaporin which functions as both a molecular water channel protein and as a non-selective cation channel gated by cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).[7] It is a homotetramer with six bilayer spanning domains and N-glycosylation sites. The AQP1 monomer consists of six transmembrane alpha helices that are connected by five loops (A to E).[8] The protein physically resembles channel proteins and is abundant in erythrocytes and renal tubes. The gene encoding this aquaporin is a possible candidate for disorders involving imbalance in ocular fluid movement.[9]
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.