Loading AI tools
Two concepts on heritable traits From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy).[2][3][4] A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor.[1][5][3][6][7][8][9] In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology.[5]
Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur.[10] Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals.[10]
The word synapomorphy—coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words σύν (sún), meaning "with, together"; ἀπό (apó), meaning "away from"; and μορφή (morphḗ), meaning "shape, form".
Lampreys and sharks share some features, like a nervous system, that are not synapomorphic because they are also shared by invertebrates. In contrast, the presence of jaws and paired appendages[11] in both sharks and dogs, but not in lampreys or close invertebrate relatives, identifies these traits as synapomorphies. This supports the hypothesis that dogs and sharks are more closely related to each other than to lampreys.
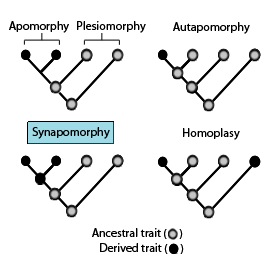
The concept of synapomorphy depends on a given clade in the tree of life. Cladograms are diagrams that depict evolutionary relationships within groups of taxa. These illustrations are accurate predictive device in modern genetics. They are usually depicted in either tree or ladder form. Synapomorphies then create evidence for historical relationships and their associated hierarchical structure. Evolutionarily, a synapomorphy is the marker for the most recent common ancestor of the monophyletic group consisting of a set of taxa in a cladogram.[12] What counts as a synapomorphy for one clade may well be a primitive character or plesiomorphy at a less inclusive or nested clade. For example, the presence of mammary glands is a synapomorphy for mammals in relation to tetrapods but is a symplesiomorphy for mammals in relation to one another—rodents and primates, for example. So the concept can be understood as well in terms of "a character newer than" (autapomorphy) and "a character older than" (plesiomorphy) the apomorphy: mammary glands are evolutionarily newer than vertebral column, so mammary glands are an autapomorphy if vertebral column is an apomorphy, but if mammary glands are the apomorphy being considered then vertebral column is a plesiomorphy.
These phylogenetic terms are used to describe different patterns of ancestral and derived character or trait states as stated in the above diagram in association with apomorphies and synapomorphies.[13][14]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.