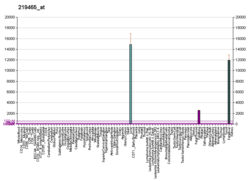
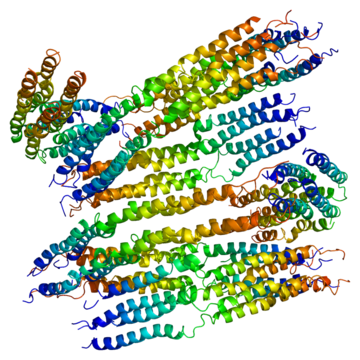
Apolipoprotein A-II is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APOA2 gene.[5] It is the second most abundant protein of the high density lipoprotein particles. The protein is found in plasma as a monomer, homodimer, or heterodimer with apolipoprotein D. ApoA-II regulates many steps in HDL metabolism, and its role in coronary heart disease is unclear. [6] Remarkably, defects in this gene may result in apolipoprotein A-II deficiency or hypercholesterolemia.[7]
Quick Facts APOA2, Available structures ...
Close
Quick Facts ApoA-II, Identifiers ...
Close
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
[[File:
|alt=Statin pathway
edit]]
- Blanco-Vaca F, Escolà-Gil JC, Martín-Campos JM, Julve J (Nov 2001). "Role of apoA-II in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis: advances in the study of an enigmatic protein". Journal of Lipid Research. 42 (11): 1727–39. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)31499-1. PMID 11714842.
- Kalopissis AD, Pastier D, Chambaz J (Apr 2003). "Apolipoprotein A-II: beyond genetic associations with lipid disorders and insulin resistance". Current Opinion in Lipidology. 14 (2): 165–72. doi:10.1097/00041433-200304000-00008. PMID 12642785. S2CID 7365994.
- Vollmer E, Brust J, Roessner A, Bosse A, Burwikel F, Kaesberg B, Harrach B, Robenek H, Böcker W (1991). "Distribution patterns of apolipoproteins A1, A2, and B in the wall of atherosclerotic vessels". Virchows Archiv A. 419 (2): 79–88. doi:10.1007/BF01600220. PMID 1908160. S2CID 31793659.
- Deeb SS, Takata K, Peng RL, Kajiyama G, Albers JJ (Apr 1990). "A splice-junction mutation responsible for familial apolipoprotein A-II deficiency". American Journal of Human Genetics. 46 (4): 822–7. PMC 1683675. PMID 2107739.
- Gordon JI, Sims HF, Edelstein C, Scanu AM, Strauss AW (Nov 1985). "Extracellular processing of proapolipoprotein A-II in Hep G2 cell cultures is mediated by a 54-kDa protease immunologically related to cathepsin B". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 260 (27): 14824–31. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)38646-5. PMID 2414299.
- Lackner KJ, Law SW, Brewer HB (Jun 1985). "The human apolipoprotein A-II gene: complete nucleic acid sequence and genomic organization". Nucleic Acids Research. 13 (12): 4597–608. doi:10.1093/nar/13.12.4597. PMC 321808. PMID 2989800.
- Knott TJ, Wallis SC, Robertson ME, Priestley LM, Urdea M, Rall LB, Scott J (Sep 1985). "The human apolipoprotein AII gene: structural organization and sites of expression". Nucleic Acids Research. 13 (17): 6387–98. doi:10.1093/nar/13.17.6387. PMC 321960. PMID 2995928.
- Chan L, Moore MN, Tsao YK (1986). "Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human apolipoprotein A-II cDNA". Plasma Lipoproteins Part A: Preparation, Structure, and Molecular Biology. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 128. pp. 745–52. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(86)28103-3. ISBN 978-0-12-182028-2. PMID 3088392.
- Middleton-Price HR, van den Berghe JA, Scott J, Knott TJ, Malcolm S (Jul 1988). "Regional chromosomal localisation of APOA2 to 1q21-1q23". Human Genetics. 79 (3): 283–5. doi:10.1007/BF00366253. PMID 3136074. S2CID 35574652.
- Shelley CS, Sharpe CR, Baralle FE, Shoulders CC (Nov 1985). "Comparison of the human apolipoprotein genes. Apo AII presents a unique functional intron-exon junction". Journal of Molecular Biology. 186 (1): 43–51. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(85)90255-4. PMID 3935800.
- Brewer HB, Lux SE, Ronan R, John KM (May 1972). "Amino acid sequence of human apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), an apolipoprotein isolated from the high-density lipoprotein complex". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 69 (5): 1304–8. Bibcode:1972PNAS...69.1304B. doi:10.1073/pnas.69.5.1304. PMC 426687. PMID 4338591.
- Lux SE, John KM, Ronan R, Brewer HB (Dec 1972). "Isolation and characterization of the tryptic and cyanogen bromide peptides of apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), plasma high density apolipoprotein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 247 (23): 7519–27. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)44556-0. PMID 4344225.
- Moore MN, Kao FT, Tsao YK, Chan L (Aug 1984). "Human apolipoprotein A-II: nucleotide sequence of a cloned cDNA, and localization of its structural gene on human chromosome 1". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 123 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(84)90371-1. PMID 6089788.
- Lackner KJ, Law SW, Brewer HB (Sep 1984). "Human apolipoprotein A-II: complete nucleic acid sequence of preproapo A-II". FEBS Letters. 175 (1): 159–64. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(84)80590-6. PMID 6090207. S2CID 9320651.
- Gordon JI, Budelier KA, Sims HF, Edelstein C, Scanu AM, Strauss AW (Nov 1983). "Biosynthesis of human preproapolipoprotein A-II". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 258 (22): 14054–9. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)44023-3. PMID 6315718.
- Sharpe CR, Sidoli A, Shelley CS, Lucero MA, Shoulders CC, Baralle FE (May 1984). "Human apolipoproteins AI, AII, CII and CIII. cDNA sequences and mRNA abundance". Nucleic Acids Research. 12 (9): 3917–32. doi:10.1093/nar/12.9.3917. PMC 318799. PMID 6328445.
- Stoffel W, Krüger E, Deutzmann R (Mar 1983). "Cell-free translation of human liver apolipoprotein AI and AII mRNA. Processing of primary translation products". Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift für Physiologische Chemie. 364 (3): 227–37. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.1.227. PMID 6407957.
- Knott TJ, Priestley LM, Urdea M, Scott J (May 1984). "Isolation and characterisation of a cDNA encoding the precursor for human apolipoprotein AII". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 120 (3): 734–40. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(84)80168-0. PMID 6428397.
- Lackner KJ, Law SW, Brewer HB, Sakaguchi AY, Naylor SL (Aug 1984). "The human apolipoprotein A-II gene is located on chromosome 1". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 122 (3): 877–83. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(84)91172-0. PMID 6433912.