Antimicrobial peptides
Class of peptides that have antimicrobial activity From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antimicrobials which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria,[1] enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells.[2] Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators.
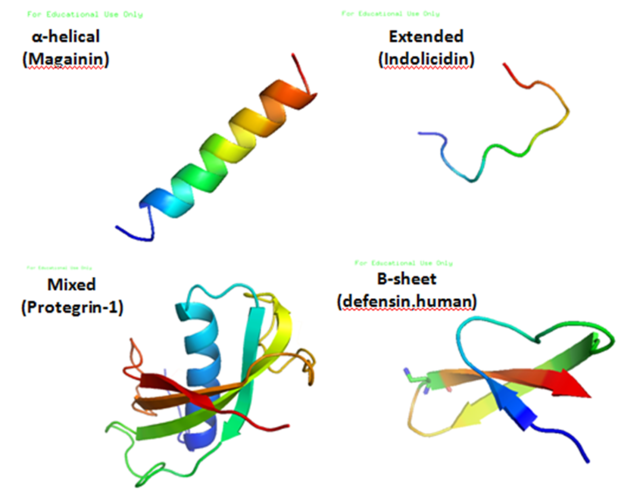
Structure
Summarize
Perspective

Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure.[3] Antimicrobial peptides are generally between 12 and 50 amino acids. These peptides include two or more positively charged residues provided by arginine, lysine or, in acidic environments, histidine, and a large proportion (generally >50%) of hydrophobic residues.[4][5][6] The secondary structures of these molecules follow 4 themes, including i) α-helical, ii) β-stranded due to the presence of 2 or more disulfide bonds, iii) β-hairpin or loop due to the presence of a single disulfide bond and/or cyclization of the peptide chain, and iv) extended.[7] Many of these peptides are unstructured in free solution, and fold into their final configuration upon partitioning into biological membranes. The peptides contain hydrophilic amino acid residues aligned along one side and hydrophobic amino acid residues aligned along the opposite side of a helical molecule.[3] This amphipathicity of the antimicrobial peptides allows them to partition into the membrane lipid bilayer. The ability to associate with membranes is a definitive feature of antimicrobial peptides,[8][9] although membrane permeabilization is not necessary. These peptides have a variety of antimicrobial activities ranging from membrane permeabilization to action on a range of cytoplasmic targets.[citation needed]
| Type | characteristic | AMPs |
|---|---|---|
| Anionic peptides | rich in glutamic and aspartic acids | Maximin H5 from amphibians, dermcidin from humans |
| Linear cationic α-helical peptides | lack in cysteine | Cecropins, andropin, moricin, ceratotoxin and melittin from insects, Magainin, dermaseptin, bombinin, brevinin-1, esculentins and buforin II from amphibians, CAP18 from rabbits, LL37 from humans |
| Cationic peptide enriched for specific amino acid | rich in proline, arginine, phenylalanine, glycine, tryptophan | abaecin and drosocin, apidaecin, diptericin, and attacin from insects, prophenin from pigs, indolicidin from cattle. |
| Anionic/cationic peptides forming disulfide bonds | contain 1~3 disulfide bond |
|
Activities
Summarize
Perspective

The modes of action by which antimicrobial peptides kill microbes are varied,[10] and may differ for different bacterial species.[11] Some antimicrobial peptides kill both bacteria and fungi, e.g., psoriasin kills E. coli and several filamentous fungi.[12] The cytoplasmic membrane is a frequent target, but peptides may also interfere with DNA and protein synthesis, protein folding, and cell wall synthesis.[10] The initial contact between the peptide and the target organism is electrostatic, as most bacterial surfaces are anionic, or hydrophobic, such as in the antimicrobial peptide Piscidin. Their amino acid composition, amphipathicity, cationic charge and size allow them to attach to and insert into membrane bilayers to form pores by ‘barrel-stave’, ‘carpet’ or ‘toroidal-pore’ mechanisms. Alternately, they may penetrate into the cell to bind intracellular molecules which are crucial to cell living.[13] Intracellular binding models includes inhibition of cell wall synthesis, alteration of the cytoplasmic membrane, activation of autolysin, inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis, and inhibition of certain enzymes. In many cases, the exact mechanism of killing is not known. One emerging technique for the study of such mechanisms is dual polarisation interferometry.[14][15] In contrast to many conventional antibiotics these peptides appear to be bactericidal[2] instead of bacteriostatic. In general the antimicrobial activity of these peptides is determined by measuring the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC), which is the lowest concentration of drug that inhibits bacterial growth.[16]
AMPs can possess multiple activities including anti-gram-positive bacterial, anti-gram-negative bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-viral, anti-parasitic, and anti cancer activities. A big AMP functional analysis indicates that among all AMP activities, amphipathicity and charge, two major properties of AMPs, best distinguish between AMPs with and without anti-gram-negative bacterial activities.[17] This implies that being AMPs with anti-gram-negative bacterial activities may prefer or even require strong amphipathicity and net positive charge.[citation needed]
Immunomodulation
In addition to killing bacteria directly they have been demonstrated to have a number of immunomodulatory functions that may be involved in the clearance of infection, including the ability to alter host gene expression, act as chemokines and/or induce chemokine production, inhibiting lipopolysaccharide induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production, promoting wound healing, and modulating the responses of dendritic cells and cells of the adaptive immune response. Animal models indicate that host defense peptides are crucial for both prevention and clearance of infection. It appears as though many peptides initially isolated as and termed "antimicrobial peptides" have been shown to have more significant alternative functions in vivo (e.g. hepcidin[18]). Dusquetide for example is an immunomodulator that acts through p62, a protein involved in toll like receptor based signalling of infection. The peptide is being examined in a Phase III clinical trial by Soligenix (SGNX) to ascertain if it can assist in repair of radiation-induced damage to oral mucosa arising during cancer radiotherapy of the head and neck.[19]
Mechanisms of action
Summarize
Perspective

Antimicrobial peptides generally have a net positive charge, allowing them to interact with the negatively charged molecules exposed on bacteria and cancer cell surfaces, such as phospholipid phosphatidylserine, O-glycosylated mucins, sialylated gangliosides, and heparin sulfates. The mechanism of action of these peptides varies widely but can be simplified into two categories: membranolytic and non-membranolytic antimicrobial peptides.[20] The disruption of membranes by membranolytic antimicrobial peptides can be described by four models:[20]
- Barrel-stave model: The barrel-stave model proposes that AMPs interact with the lipid bilayer of the microbial cell membrane to form transmembrane channels or "barrel staves". These channels are thought to disrupt the membrane's integrity, leading to the death of the microbe.
- Carpet model: The carpet model proposes that AMPs adsorb onto the lipid bilayer of the microbial cell membrane, forming a dense layer that causes the membrane to become permeabilized. This model suggests that the AMP acts as a "carpet" that covers the surface of the cell, preventing the microbe from functioning properly.
- Toroidal model: The toroidal model proposes that AMPs interact with the lipid bilayer of the microbial cell membrane to form toroidal structures, which are thought to pinch off sections of the membrane and lead to the formation of vesicles. This process is thought to disrupt the membrane's integrity and cause the death of the microbe.
- Disordered toroidal-pore model: According to this model, the disordered AMPs wrap around the lipid bilayer and create a pore, which disrupts the membrane's integrity and leads to the death of the microbe. Unlike the toroidal model, which suggests that the AMP creates a stable toroidal structure, the disordered toroidal-pore model suggests that the AMP is flexible and does not form a stable toroidal structure. The peptide-lipid pore complex becomes intrinsically disordered, with the orientation of the peptide not well defined.[21]

Several methods have been used to determine the mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide activity.[11][13] In particular, solid-state NMR studies have provided an atomic-level resolution explanation of membrane disruption by antimicrobial peptides.[23][24] In more recent years, X-ray crystallography has been used to delineate in atomic detail how the family of plant defensins rupture membranes by identifying key phospholipids in the cell membranes of the pathogen.[25][26] Human defensins have been thought to act through a similar mechanism, targeting cell membrane lipids as part of their function. In fact human beta-defensin 2 have now been shown to kill the pathogenic fungi Candida albicans through interactions with specific phospholipids.[27] From the computational point of view, Molecular Dynamics simulations can provide detailed information about the structure and dynamics of the peptide-membrane interactions, including the orientation, conformation, and insertion of the peptide in the membrane, as well as specific peptide interactions with lipids, ions and solvent.[28]
| Methods | Applications |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | to visualize the effects of antimicrobial peptides on microbial cells |
| Atomic emission spectroscopy | to detect loss of intracellular potassium (an indication that bacterial membrane integrity has been compromised) |
| Fluorescent dyes | to measure ability of antimicrobial peptides to permeabilize membrane vesicles |
| Ion channel formation | to assess the formation and stability of an antimicrobial-peptide-induced pore |
| Circular dichroism and orientated circular dichroism | to measure the orientation and secondary structure of an antimicrobial peptide bound to a lipid bilayer |
| Dual polarization interferometry | to measure the different mechanisms of antimicrobial peptides |
| Solid-state NMR spectroscopy | to measure the secondary structure, orientation and penetration of antimicrobial peptides into lipid bilayers in the biologically relevant liquid-crystalline state |
| Neutron and X-ray diffraction | to measure the diffraction patterns of peptide-induced pores within membranes in oriented multilayers or liquids |
| Molecular dynamics simulations | to study the molecular behaviour and search for specific peptide-lipid interactions |
| Mass spectrometry | to measure the proteomic response of microorganisms to antimicrobial peptides |
Therapeutic research and use
Summarize
Perspective
Antimicrobial peptides have been used as therapeutic agents; their use is generally limited to intravenous administration or topical applications due to their short half-lives. As of January 2018 the following antimicrobial peptides were in clinical use:[29]
- Bacitracin for pneumonia, topical
- Boceprevir, Hepatitis C (oral, cyclic peptide)
- Dalbavancin, bacterial infections, IV
- Daptomycin, bacterial infections, IV
- Enfuvirtide, HIV, subcutaneous injection
- Oritavancin, bacterial infections, IV
- Teicoplanin, bacterial infections, IV
- Telaprevir, Hepatitis C, oral cyclic peptide
- Telavancin, bacterial infection, IV
- Vancomycin, bacterial infection, IV.
- Guavanin 2, bacterial infection against Gram-positive and Gram-negative also.
Activity beyond antibacterial functions
AMPs have been observed having functions other than bacterial and fungal killing. These activities include antiviral effects, but also roles in host defence such as anticancer functions and roles in neurology.[30] This has led to a movement for re-branding AMPs as "Host-defence peptides" to encompass the broad scope of activities AMPs can have.[31]
Anticancer properties
Some cecropins (e.g. cecropin A, and cecropin B) have anticancer properties and are called anticancer peptides (ACPs).[32]: 3 Hybrid ACPs based on Cecropin A have been studied for anticancer properties.[32]: 7.1 The fruit fly Defensin prevents tumour growth, suspected to bind to tumour cells owing to cell membrane modifications common to most cancer cells, such as phosphatidylserine exposure.[33]
Antibiofilm properties
Cecropin A can destroy planktonic and sessile biofilm-forming uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) cells, either alone or when combined with the antibiotic nalidixic acid, synergistically clearing infection in vivo (in the insect host Galleria mellonella) without off-target cytotoxicity. The multi-target mechanism of action involves outer membrane permeabilization followed by biofilm disruption triggered by the inhibition of efflux pump activity and interactions with extracellular and intracellular nucleic acids.[34]
Other research
Recently there has been some research to identify potential antimicrobial peptides from prokaryotes,[35] aquatic organisms such as fish,[36][37] and shellfish,[38] and monotremes such as echidnas.[39][40]
Selectivity
Summarize
Perspective
In the competition of bacterial cells and host cells with the antimicrobial peptides, antimicrobial peptides will preferentially interact with the bacterial cell to the mammalian cells, which enables them to kill microorganisms without being significantly toxic to mammalian cells.[41]
With regard to cancer cells, they themselves also secrete human antimicrobial peptides including defensin, and in some cases, they are reported to be more resistant than the surrounding normal cells. Therefore, we cannot conclude that selectivity is always high against cancer cells.[42][43]
Factors
There are some factors that are closely related to the selectivity property of antimicrobial peptides, among which the cationic property contributes most. Since the surface of the bacterial membranes is more negatively charged than mammalian cells, antimicrobial peptides will show different affinities towards the bacterial membranes and mammalian cell membranes.[44]
In addition, there are also other factors that will affect the selectivity. It's well known that cholesterol is normally widely distributed in the mammalian cell membranes as a membrane stabilizing agent but absent in bacterial cell membranes (except when sequestered by H. pylori);[45] and the presence of these cholesterols will also generally reduce the activities of the antimicrobial peptides, due either to stabilization of the lipid bilayer or to interactions between cholesterol and the peptide. So the cholesterol in mammalian cells will protect the cells from attack by the antimicrobial peptides.[46]
Besides, the transmembrane potential is well known to affect peptide-lipid interactions.[47] There's an inside-negative transmembrane potential existing from the outer leaflet to the inner leaflet of the cell membranes and this inside-negative transmembrane potential will facilitate membrane permeabilization probably by facilitating the insertion of positively charged peptides into membranes. By comparison, the transmembrane potential of bacterial cells is more negative than that of normal mammalian cells, so bacterial membrane will be prone to be attacked by the positively charged antimicrobial peptides.[citation needed]
Similarly, it is also believed that increasing ionic strength,[46] which in general reduces the activity of most antimicrobial peptides, contributes partially to the selectivity of the antimicrobial peptides by weakening the electrostatic interactions required for the initial interaction.

Mechanism
The cell membranes of bacteria are rich in acidic phospholipids, such as phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin.[41][48]
In contrast, the outer part of the membranes of plants and mammals is mainly composed of lipids without any net charges since most of the lipids with negatively charged headgroups are principally sequestered into the inner leaflet of the plasma membranes.[44] Thus in the case of mammalian cells, the outer surfaces of the membranes are usually made of zwitterionic phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin, even though a small portion of the membrane's outer surfaces contain some negatively charged gangliosides. Therefore, the hydrophobic interaction between the hydrophobic face of amphipathic antimicrobial peptides and the zwitterionic phospholipids on the cell surface of mammalian cell membranes plays a major role in the formation of peptide-cell binding.[49]
Dual polarisation interferometry has been used in vitro to study and quantify the association to headgroup, insertion into the bilayer, pore formation and eventual disruption of the membrane.[50][51]
Control
A lot of effort has been put into controlling cell selectivity. For example, attempts have been made to modify and optimize the physicochemical parameters of the peptides to control the selectivities, including net charge, helicity, hydrophobicity per residue (H), hydrophobic moment (μ) and the angle subtended by the positively charged polar helix face (Φ).[47] Other mechanisms like the introduction of D-amino acids and fluorinated amino acids in the hydrophobic phase are believed to break the secondary structure and thus reduce hydrophobic interaction with mammalian cells. It has also been found that Pro→Nlys substitution in Pro-containing β-turn antimicrobial peptides was a promising strategy for the design of new small bacterial cell-selective antimicrobial peptides with intracellular mechanisms of action.[52] It has been suggested that direct attachment of magainin to the substrate surface decreased nonspecific cell binding and led to improved detection limit for bacterial cells such as Salmonella and E. coli.[53]
Bacterial resistance
Summarize
Perspective
Bacteria use various resistance strategies to avoid antimicrobial peptide killing.[13]
- Some microorganisms alter net surface charges. Staphylococcus aureus transports D-alanine from the cytoplasm to the surface teichoic acid which reduces the net negative charge by introducing basic amino groups.[54] S. aureus also modifies its anionic membranes via MprF with L-lysine, increasing the positive net charge.[54]
- The interaction of antimicrobial peptides with membrane targets can be limited by capsule polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae.[55]
- Salmonella species reduce the fluidity of their outer membrane by increasing hydrophobic interactions between an increased number of Lipid A acyl tails by adding myristate to Lipid A with 2-hydroxymyristate and forming hepta-acylated Lipid A by adding palmitate. The increased hydrophobic moment is thought to retard or abolish antimicrobial peptide insertion and pore formation. The residues undergo alteration in membrane proteins. In some Gram-negative bacteria, alteration in the production of outer membrane proteins correlates with resistance to killing by antimicrobial peptides.[56]
- Non-typeable Hemophilus influenzae transports AMPs into the interior of the cell, where they are degraded. Furthermore, H. influenzae remodels its membranes to make it appear as if the bacterium has already been successfully attacked by AMPs, protecting it from being attacked by more AMPs.[57]
- ATP-binding cassette transporters import antimicrobial peptides and the resistance-nodulation cell-division efflux pump exports antimicrobial peptides.[58] Both transporters have been associated with antimicrobial peptide resistance
- Bacteria produce proteolytic enzymes, which may degrade antimicrobial peptides leading to their resistance.[59]
- Outer membrane vesicles produced by Gram-negative bacteria bind the antimicrobial peptides and sequester them away from the cells, thereby protecting the cells.[60] The outer membrane vesicles are also known to contain various proteases, peptidases and other lytic enzymes, which may have a role in degrading the extracellular peptide and nucleic acid molecules, which if allowed to reach to the bacterial cells may be dangerous for the cells.
- Cyclic-di-GMP signaling had also been involved in the regulation of antimicrobial peptide resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[61]
While these examples show that resistance can evolve naturally, there is increasing concern that using pharmaceutical copies of antimicrobial peptides can make resistance happen more often and faster. In some cases, resistance to these peptides used as a pharmaceutical to treat medical problems can lead to resistance, not only to the medical application of the peptides, but to the physiological function of those peptides.[62][63]
The ‘Trojan Horse’ approach to solving this problem capitalizes on the innate need for iron by pathogens. “Smuggling” antimicrobials into the pathogen is accomplished by linking them to siderophores for transport. While simple in concept, it has taken many decades of work to accomplish the difficult hurdle of transporting antimicrobials across the cell membranes of pathogens. Lessons learned from the successes and failures of siderophore-conjugate drugs evaluated during the development of novel agents using the ‘Trojan horse’ approach have been reviewed.[64]
Examples
Summarize
Perspective

Antimicrobial peptides are produced by species across the tree of life, including:
- bacteria (e.g. bacteriocin, and many others)
- fungi (e.g. peptaibols, plectasin, and many others)
- cnidaria (e.g. hydramacin, aurelin)
- many from insects and arthropods (e.g. cecropin, attacin, melittin, mastoparan, drosomycin, thioester-containing protein 1)[65]
- amphibia, frogs (magainin, dermaseptin, aurein, and others)[66][67]
- birds (e.g. avian defensins)[68]
- and mammals (e.g. cathelicidins, alpha- and beta-defensins, regIII peptides)
Research has increased in recent years to develop artificially-engineered mimics of antimicrobial peptides such as SNAPPs, in part due to the prohibitive cost of producing naturally-derived AMPs.[69] An example of this is the facially cationic peptide C18G, which was designed from the C-terminal domain of human platelet factor IV.[70] Currently, the most widely used antimicrobial peptide is nisin; being the only FDA approved antimicrobial peptide, it is commonly used as an artificial preservative.[71]
Bioinformatics
Summarize
Perspective
Several bioinformatic databases exist to catalogue antimicrobial peptides. The Antimicrobial Peptide Database (APD) is the original and model database for antimicrobial peptides (https://aps.unmc.edu). Based on the APD, other databases have also been built, including ADAM (A Database of Anti-Microbial peptides),[72] BioPD (Biologically active Peptide Database), CAMP (Collection of sequences and structures of antimicrobial peptides),[73] DBAASP (Database of Antimicrobial Activity and Structure of Peptides), DRAMP (Data Repository of Antimicrobial Peptides)Welcome To Dramp Database,[74] and LAMP (Linking AMPs).
The Antimicrobial peptide databases may be divided into two categories on the basis of the source of peptides it contains, as specific databases and general databases. These databases have various tools for antimicrobial peptides analysis and prediction. For example, the APD has a widely used calculation interface. It also provides links to many other tools. CAMP contains AMP prediction, feature calculator, BLAST search, ClustalW, VAST, PRATT, Helical wheel etc. In addition, ADAM allows users to search or browse through AMP sequence-structure relationships. Antimicrobial peptides often encompass a wide range of categories such as antifungal, antibacterial, and antituberculosis peptides.
dbAMP:[75] Provides an online platform for exploring antimicrobial peptides with functional activities and physicochemical properties on transcriptome and proteome data. dbAMP is an online resource that addresses various topics such as annotations of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) including sequence information, antimicrobial activities, post-translational modifications (PTMs), structural visualization, antimicrobial potency, target species with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), physicochemical properties, or AMP–protein interactions.[citation needed]
Tools such as PeptideRanker,[76] PeptideLocator,[77] and AntiMPmod[78][79] allow for the prediction of antimicrobial peptides while others have been developed to predict antifungal and anti-Tuberculosis activities.[80][81]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
