Acinus
Multi-lobed biological cell structure From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Multi-lobed biological cell structure From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
An acinus (/ˈæsɪnəs/; pl.: acini; adjective, acinar /ˈæsɪnər/ or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry (acinus is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the secretion is produced, is acinar in form, as is the alveolar sac containing multiple alveoli in the lungs.
| Acinus | |
|---|---|
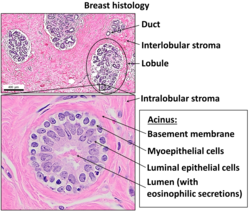 Normal histology of the breast, including an acinus in lower image. The terminal duct connected to the magnified acinus is not within this microsection. | |
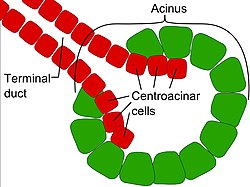 Centroacinar cells | |
| Identifiers | |
| TH | H2.00.02.0.03050 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Acinar exocrine glands are found in many organs, including:
The thyroid follicles can also be considered of acinar formation but in this case the follicles, being part of an endocrine gland, act as a hormonal deposit rather than to facilitate secretion.
Mucous acini usually stain pale, while serous acini usually stain dark.
The end of the terminal bronchioles in the lungs mark the beginning of a pulmonary acinus that includes the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli.[4]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.