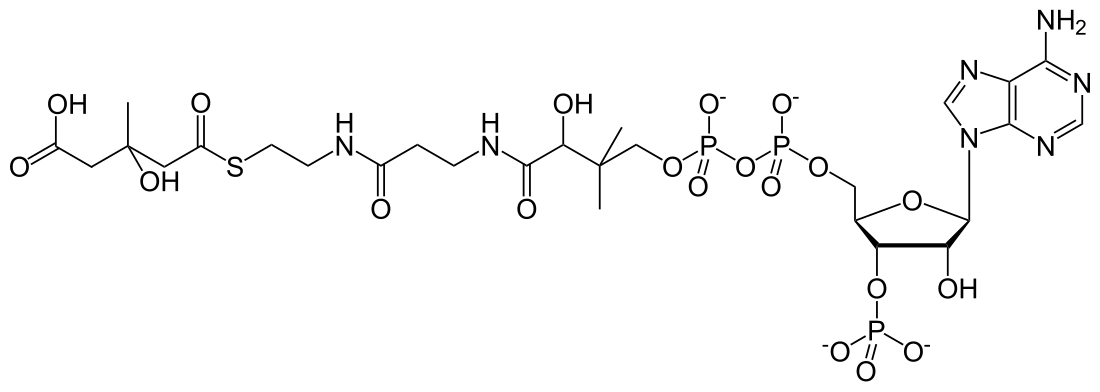
HMG-CoA
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The research of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(9R,21S)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-3,5,9,21-tetrahydroxy-8,8,21-trimethyl-10,14,19-trioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-18-thia-11,15-diaza-3,5-diphosphatricosan-23-oic acid 3,5-dioxide | |
| Other names
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA; 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.820 |
| MeSH | HMG-CoA |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H44N7O20P3S | |
| Molar mass | 911.661 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
HMG-CoA is a metabolic intermediate in the metabolism of the branched-chain amino acids, which include leucine, isoleucine, and valine.[3] Its immediate precursors are β-methylglutaconyl-CoA (MG-CoA) and β-hydroxy β-methylbutyryl-CoA (HMB-CoA).[4][5][6]
HMG-CoA reductase catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.
Biosynthesis
Mevalonate pathway
Mevalonate synthesis begins with the beta-ketothiolase-catalyzed Claisen condensation of two molecules of acetyl-CoA to produce acetoacetyl CoA. The following reaction involves the joining of acetyl-CoA and acetoacetyl-CoA to form HMG-CoA, a process catalyzed by HMG-CoA synthase.[8]
In the final step of mevalonate biosynthesis, HMG-CoA reductase, an NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase, catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA into mevalonate, which is the primary regulatory point in this pathway. Mevalonate serves as the precursor to isoprenoid groups that are incorporated into a wide variety of end-products, including cholesterol in humans.[9]

Ketogenesis pathway
HMG-CoA lyase breaks it into acetyl CoA and acetoacetate.

See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.