2022 in the environment
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is an article of notable issues relating to the terrestrial environment of Earth in 2022. They relate to environmental events such as natural disasters, environmental sciences such as ecology and geoscience with a known relevance to contemporary influence of humanity on Earth, environmental law, conservation, environmentalism with major worldwide impact and environmental issues.
Events
| Date / period | Type of event | Event | Topics | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| February 2 | Policy | Global plastic pollution treaty agreement. | ||
Environmental policies approved
Environmental disasters

| To display all pages, subcategories and images click on the "►": |
|---|
Pollution events
Environmental science
| Date / period | Type | Description | Topics | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 10 | Analysis, Assessment | Researchers build upon previous studies documenting biodiversity loss to confirm that a sixth mass extinction event, entirely caused by anthropogenic activity, is currently underway.[2][3] | [ecosystem] [biodiversity] |  |
| January 10 | Analysis, Proposal | A study quantifies climate change mitigation potentials of 'high-income' nations shifting diets – away from meat-consumption – and restoration of the spared land.[4][5] | [agriculture] [food] |  |
| January 18 | Analysis, Assessment | A study suggests and defines a 'planetary boundary' for novel entities such as plastic- and chemical pollution and finds that it has been crossed.[6][7] | [plastic pollution] |  |
| January 18 | Analysis, Assessment | A study for the first time attempts to assess and quantify complete societal costs of cars (i.e. car-use, etc).[8] | [policy] |  |
| February 1 | Analysis, Assessment, Observation | The American Geophysical Union reports, based on a study by Chinese scientists published in November, that climate change has likely begun to suffocate the world's fisheries, passing a critical threshold of oxygen loss in 2021.[9][10] | [climate change] [food system] |  |
| February 3 | Observation, Development | The first comprehensive global map of oil and gas "ultra-emitters" of the potent greenhouse gas methane based on satellite data is published.[11][12][13] | [methane emissions] |  |
| February 9 | Development[relevant?] | Researchers report the development of a viable flash JH-based process to recover rare-earth elements used in modern electronics from industrial wastes with practical potential to reduce environmental/health impacts from mining, waste-generation and imports if it can be scaled up.[14][15] | [circular economy] |  |
| February 14 | Observation, Assessment | The most comprehensive study of pharmaceutical pollution of the world's rivers finds that it threatens "environmental and/or human health in more than a quarter of the studied locations".[16][17] | [water pollution] |  |
| February 15 | Analysis, Projections | NASA publishes its latest Sea Level Rise Technical Report, an update of the 2017 edition, which includes projections for sea-level rise through to the year 2150. The agency warns that sea levels may rise as much over the next 30 years as during the previous 100.[18][19] | [sea level rise] |  |
| February 16 | Analysis | A study models the system of coupled feedback processes (including potential mitigation tipping points) that may shape the trajectory of global greenhouse gas emissions over the century in the contemporary socioeconomic system if it both persists as is and its components remain largely unreformed. Broad factor-domains include public perceptions of climate change, future mitigation technologies' characteristics, and the responsiveness of political institutions.[20][21] | [climate change] |  |
| February 17 | Development[relevant?] | Bionanotechnologists report the development of a viable biosensor, ROSALIND 2.0, that can detect levels of diverse water pollutants.[22][23] | [water pollution] |  |
| February 23 | Development[relevant?] | Researchers report the development of a quantum gradiometer – an atom interferometer quantum sensor – which could be used to map and investigate subterraneans.[24][25] | [sensing] |  |
| February 23 | Analysis, Review, Projections | UN researchers publish a comprehensive study about climate change impacted wildfires with projections (e.g. a 31–57% increase of extreme wildfires by 2100) and information about impacts and countermeasures.[26][27] | [wildfires] |  |
| February 28 | Analysis, Assessment | A study shows annual carbon emissions (or carbon loss) from tropical deforestation have doubled during the last two decades and continue to increase.[28][29] | [deforestation] [climate change] |  |
| February 28 | Review | The IPCC releases the second part of its Sixth Assessment Report on climate change. It shows that any further delay in concerted global action would mean missing the rapidly closing window to secure human wellbeing and the planet's health against cascading impacts.[30][31] | [climate change] |  |
| March 1 | Analysis, Observation | Atmospheric scientists report that the 2022 volcano eruption in Tonga, Pacific Ocean – the largest recorded volcanic eruption since 1991 which reportedly cooled global climate by ~0.6 °C during 15 months[32] – did not have a cooling effect (volcanic winter) of significance to global climate change (i.e. a cooling of ~0.004 °C during the first year).[33][34] | [climate change] [volcanoes] |  |
| March 7 | Analysis, Observation | Researchers report that more than three-quarters of the Amazon rainforest has been losing resilience due to deforestation and climate change since the early 2000s as measured by recovery-time from short-term perturbations ("critical slowing down" (CSD)), reinforcing the theory that it is approaching a critical transition.[35][36] On March 11, INPE reports satellite data that show record-high levels of Amazon deforestation in Brazil for a February (199 km²).[37] | [deforestation] |  |
| March 7 | Analysis, Observation | A study suggests that half of the US population has been exposed to substantially detrimental lead levels in early childhood – mainly from car exhaust whose lead pollution peaked in the 1970s.[38][39][globalize] | [toxins] [transport] |  |
| March 9 | Analysis | Researchers report that, on average, the elderly played "a leading role in driving up GHG emissions in the past decade and are on the way to becoming the largest contributor" due to factors such as demographic transition, low informed concern about climate change and high expenditures on carbon-intensive products like energy which is used i.a. for heating rooms and private transport.[40][41] | [climate change] |  |
| March 10 | Analysis, Assessment, Proposal | A study estimates that "relocating current croplands to [environmentally] optimal locations, whilst allowing ecosystems in then-abandoned areas to regenerate, could simultaneously decrease the current carbon, biodiversity, and irrigation water footprint of global crop production by 71%, 87%, and 100%", with relocation only within national borders also having substantial potential.[42][43] | [food system] | 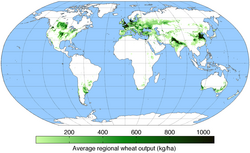 |
| March 16 | Analysis, Observation | Researchers report that over 80% of the growth of methane emissions during 2010–2019 was caused by tropical terrestrial emissions.[44][45] | [methane emissions] |  |
| March 21 | Observation, Analysis | Before formal publication of the 'Global Carbon Budget 2021' preprint,[46] scientists report, based on Carbon Monitor[47] data, that after COVID-19-pandemic-caused record-level declines in 2020, global CO2 emissions rebounded sharply by 4.8% in 2021, indicating that at the current trajectory, the 1.5 °C carbon budget would be used up within 9.5 years with a two-thirds likelihood.[48] | [climate change] |  |
| March 24 | Review | Scientists review the biophysical mechanisms by which forests influence climate, showing that beyond 50°N large scale deforestation leads to a net global cooling, that tropical deforestation leads to substantial warming from non-CO2-impacts, and that as well as how standing tropical forests help cool the average global temperature by more than 1 °C.[49][50] | [climate change] [deforestation] |  |
| March 31 | Analysis | Depletion of ozone in the stratosphere and, more importantly (60%), ozone increase in the troposphere is shown to be responsible for ~30% of upper Southern Ocean interior warming between 1955 and 2000.[51][52] | [ozone] |  |
See also
Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2022 in the environment.
General
Natural environment
Artificial development
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.