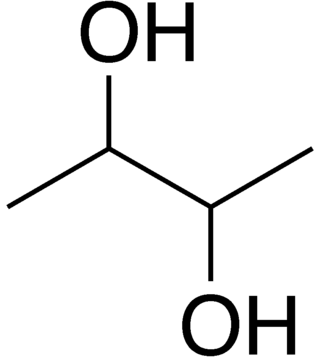
2,3-Butanediol
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
2,3-Butanediol is the organic compound with the formula (CH3CHOH)2. It is classified as a vic-diol (glycol). It exists as three stereoisomers, a chiral pair and the meso isomer. All are colorless liquids. Applications include precursors to various plastics and pesticides.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butane-2,3-diol | |
| Other names
2,3-Butylene glycol Pseudobutylene glycol 2,3-Dihydroxybutane Butan-2,3-diol Diethanol[citation needed] & Bis-ethanol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.431 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 90.122 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 0.987 g/mL |
| Melting point | 19 °C (66 °F; 292 K) |
| Boiling point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in alcohol, ketones, ether |
| log P | −0.92 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.23 hPa (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 14.9 |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4366 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
213.0 J/K mol |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−544.8 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 85 °C (185 °F; 358 K) |
| 402 °C (756 °F; 675 K) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
5462 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
Related butanediols |
1,4-Butanediol 1,3-Butanediol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Isomerism
Of the three stereoisomers, two are enantiomers (levo- and dextro-2,3-butanediol) and one is a meso compound.[1][2] The enantiomeric pair have (2R, 3R) and (2S, 3S) configurations at carbons 2 and 3, while the meso compound has configuration (2R, 3S) or, equivalently, (2S, 3R).
Industrial production and uses
2,3-Butanediol is prepared by hydrolysis of 2,3-epoxybutane:[3]
- (CH3CH)2O + H2O → CH3(CHOH)2CH3
The isomer distribution depends on the stereochemistry of the epoxide.
The meso isomer is used to combine with naphthalene-1,5-diisocyanate. The resulting polyurethane is called "Vulkollan".[3]
Biological production
The (2R,3R)-stereoisomer of 2,3-butanediol is produced by a variety of microorganisms in a process known as butanediol fermentation.[4] It is found naturally in cocoa butter, in the roots of Ruta graveolens, sweet corn, and in rotten mussels. It is used in the resolution of carbonyl compounds in gas chromatography.[5]
During World War II research was done towards producing 2,3-butanediol by fermentation in order to produce 1,3-butadiene, the monomer of the polybutadiene used in a leading type of synthetic rubber.[6] It can be derived from the fermentation of sugarcane molasses.[7]
Fermentative production of 2,3-butanediol from carbohydrates involves a network of biochemical reactions that can be manipulated to maximize production.[8]
2,3-butanediol has been proposed as a rocket fuel that could be created on Mars by means of cyanobacteria and E. coli, shipped from Earth, working on resources available at the surface of Mars.[9]
2,3-Butanediol has been detected, in peppers, grape wine, anatidaes.
Reactions
2,3-Butanediol undergo dehydration to form butanone (methyl ethyl ketone):[10]
- (CH3CHOH)2 → CH3C(O)CH2CH3 + H2O
It can also undergo deoxydehydration to form butene:[11]
- (CH3CHOH)2 + 2 H2 → C4H8 + 2 H2O
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.