Triazinane
Class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
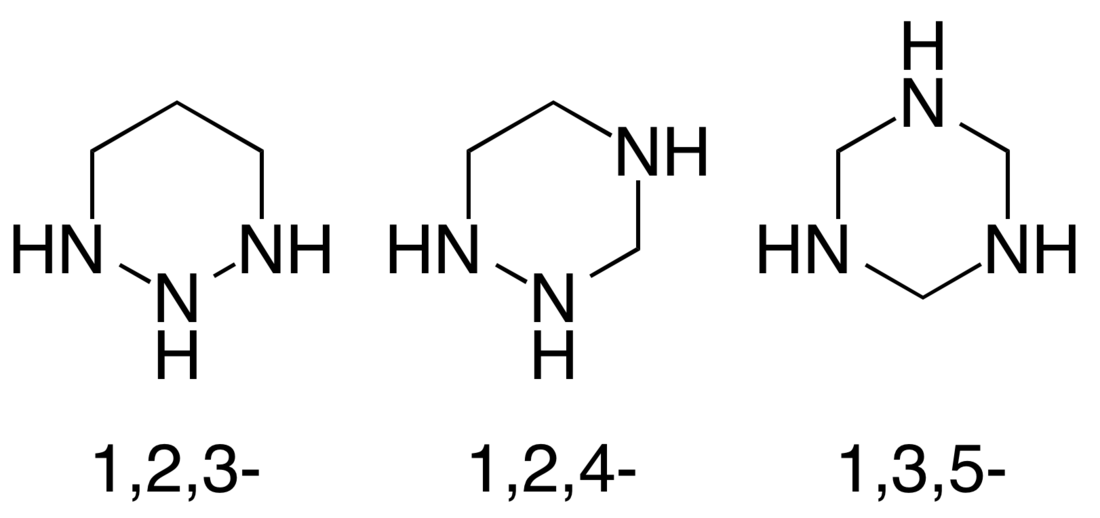
Triazinanes are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles.[1] The parent molecules' molecular formula is (CH2)3(NH)3. They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazinanes being common. The triazinanes have six-membered cyclohexane-like ring but with three carbons replaced by nitrogens. Most commonly, the amines are tertiary.
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (March 2020) |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 8477997 | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9N3 | |
| Molar mass | 87.126 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
- 6-membered rings with one nitrogen atom: Piperidine
- 6-membered rings with two nitrogen atoms: Diazinane
- Hexahydropyrimidine
- Hexahydropyridazine
- Triazine
- Borazine (borazole)
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.