Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
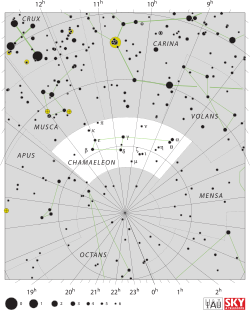
Eta Chamaeleontis
Star in the constellation Chamaeleon From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Eta Chamaeleontis, Latinized from η Chamaeleontis, is a star in the constellation Chamaeleon. It has an apparent magnitude of about 5.5, meaning that it is just barely visible to the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is located some 325 light-years (100 parsecs) light years (95 parsecs) away from the Sun.[1]
Eta Chamaeleontis has a spectral type of B8V, meaning it is a B-type main sequence star.[3] Stars of this type are typically a few times more massive than the Sun and have effective temperatures of about 10,000 to 30,000 K. Eta Chamaeleontis is just over 3 times more massive than the Sun[7] and has a temperature of about 12,000 K.[9]
Remove ads
Eta Chamaeleontis cluster
Eta Chamaeleontis is the brightest and most massive member of the eponymous Eta Chamaeleontis cluster (also known as the Eta Chamaeleontis association or Mamajek 1, pronounced /ˈmæmədʒɛk/), a very nearby (316 light years), and young (8 million years old) stellar moving group discovered in 1999.[10] The cluster contains nearly 20 stellar members spread out over a 40-arcminute diameter region of sky, including the neighboring A-type star HD 75505 and the eclipsing binary RS Cha.[11] The eclipsing binary RS Cha is a well-constrained system which enables precise age-dating, which recent results yield an age of 9 million years.[12] All of the low-mass members (including RS Cha) are pre-main sequence, and several of them appear to still be accreting from protoplanetary disks. Although containing only about 20 members, the cluster appears to be the densest stellar cluster within 100 pc (~30 solar masses per cubic parsec).[13]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads