Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton.[1] It was discovered and named by Hideo Mōri in 1968.[2] Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division.
In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.[3][4] Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 kDa). In contrast, tubulin polymers (microtubules) tend to be much bigger than actin filaments due to their cylindrical nature.
Tubulin was long thought to be specific to eukaryotes. More recently, however, several prokaryotic proteins have been shown to be related to tubulin.[5][6][7][8]
Characterization
Tubulin is characterized by the evolutionarily conserved Tubulin/FtsZ family, GTPase protein domain.
This GTPase protein domain is found in all eukaryotic tubulin chains,[9] as well as the bacterial protein TubZ,[8] the archaeal protein CetZ,[10] and the FtsZ protein family widespread in bacteria and archaea.[5][11]
Function
Microtubules
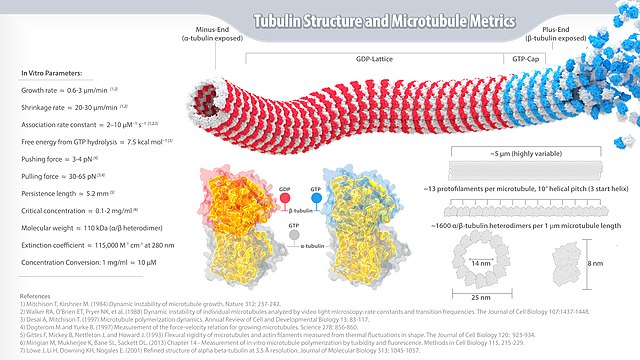
α- and β-tubulin polymerize into dynamic microtubules. In eukaryotes, microtubules are one of the major components of the cytoskeleton, and function in many processes, including structural support, intracellular transport, and DNA segregation.

Microtubules are assembled from dimers of α- and β-tubulin. These subunits are slightly acidic, with an isoelectric point between 5.2 and 5.8.[14] Each has a molecular weight of approximately 50 kDa.[15]
To form microtubules, the dimers of α- and β-tubulin bind to GTP and assemble onto the (+) ends of microtubules while in the GTP-bound state.[16] The β-tubulin subunit is exposed on the plus end of the microtubule, while the α-tubulin subunit is exposed on the minus end. After the dimer is incorporated into the microtubule, the molecule of GTP bound to the β-tubulin subunit eventually hydrolyzes into GDP through inter-dimer contacts along the microtubule protofilament.[17] The GTP molecule bound to the α-tubulin subunit is not hydrolyzed during the whole process. Whether the β-tubulin member of the tubulin dimer is bound to GTP or GDP influences the stability of the dimer in the microtubule. Dimers bound to GTP tend to assemble into microtubules, while dimers bound to GDP tend to fall apart; thus, this GTP cycle is essential for the dynamic instability of the microtubule.
Bacterial microtubules
Homologs of α- and β-tubulin have been identified in the Prosthecobacter genus of bacteria.[6] They are designated BtubA and BtubB to identify them as bacterial tubulins. Both exhibit homology to both α- and β-tubulin.[18] While structurally highly similar to eukaryotic tubulins, they have several unique features, including chaperone-free folding and weak dimerization.[19] Cryogenic electron microscopy showed that BtubA/B forms microtubules in vivo, and suggested that these microtubules comprise only five protofilaments, in contrast to eukaryotic microtubules, which usually contain 13.[13] Subsequent in vitro studies have shown that BtubA/B forms four-stranded 'mini-microtubules'.[20]
DNA segregation
Cell division
Prokaryotic division
FtsZ is found in nearly all Bacteria and Archaea, where it functions in cell division, localizing to a ring in the middle of the dividing cell and recruiting other components of the divisome, the group of proteins that together constrict the cell envelope to pinch off the cell, yielding two daughter cells. FtsZ can polymerize into tubes, sheets, and rings in vitro, and forms dynamic filaments in vivo.
TubZ functions in segregating low copy-number plasmids during bacterial cell division. The protein forms a structure unusual for a tubulin homolog; two helical filaments wrap around one another.[21] This may reflect an optimal structure for this role since the unrelated plasmid-partitioning protein ParM exhibits a similar structure.[22]
Cell shape
CetZ functions in cell shape changes in pleomorphic Haloarchaea. In Haloferax volcanii, CetZ forms dynamic cytoskeletal structures required for differentiation from a plate-shaped cell form into a rod-shaped form that exhibits swimming motility.[10]
Types
Eukaryotic
The tubulin superfamily contains six families (alpha-(α), beta-(β), gamma-(γ), delta-(δ), epsilon-(ε), and zeta-(ζ) tubulins).[23]
α-Tubulin
Human α-tubulin subtypes include:[citation needed]
β-Tubulin

All drugs that are known to bind to human tubulin bind to β-tubulin.[24] These include paclitaxel, colchicine, and the vinca alkaloids, each of which have a distinct binding site on β-tubulin.[24]
In addition, several anti-worm drugs preferentially target the colchicine site of β-Tubulin in worm rather than in higher eukaryotes. While mebendazole still retains some binding affinity to human and Drosophila β-tubulin,[25] albendazole almost exclusively binds to the β-tubulin of worms and other lower eukaryotes.[26][27]
Class III β-tubulin is a microtubule element expressed exclusively in neurons,[28] and is a popular identifier specific for neurons in nervous tissue. It binds colchicine much more slowly than other isotypes of β-tubulin.[29]
β1-tubulin, sometimes called class VI β-tubulin,[30] is the most divergent at the amino acid sequence level.[31] It is expressed exclusively in megakaryocytes and platelets in humans and appears to play an important role in the formation of platelets.[31] When class VI β-tubulin were expressed in mammalian cells, they cause disruption of microtubule network, microtubule fragment formation, and can ultimately cause marginal-band like structures present in megakaryocytes and platelets.[32]
Katanin is a protein complex that severs microtubules at β-tubulin subunits, and is necessary for rapid microtubule transport in neurons and in higher plants.[33]
Human β-tubulins subtypes include:[citation needed]
γ-Tubulin

γ-Tubulin, another member of the tubulin family, is important in the nucleation and polar orientation of microtubules. It is found primarily in centrosomes and spindle pole bodies, since these are the areas of most abundant microtubule nucleation. In these organelles, several γ-tubulin and other protein molecules are found in complexes known as γ-tubulin ring complexes (γ-TuRCs), which chemically mimic the (+) end of a microtubule and thus allow microtubules to bind. γ-tubulin also has been isolated as a dimer and as a part of a γ-tubulin small complex (γTuSC), intermediate in size between the dimer and the γTuRC. γ-tubulin is the best understood mechanism of microtubule nucleation, but certain studies have indicated that certain cells may be able to adapt to its absence, as indicated by mutation and RNAi studies that have inhibited its correct expression. Besides forming a γ-TuRC to nucleate and organize microtubules, γ-tubulin can polymerize into filaments that assemble into bundles and meshworks.[34]
Human γ-tubulin subtypes include:
Members of the γ-tubulin ring complex:
δ and ε-Tubulin
Delta (δ) and epsilon (ε) tubulin have been found to localize at centrioles and may play a role in centriole structure and function, though neither is as well-studied as the α- and β- forms.
Human δ- and ε-tubulin genes include:[citation needed]
ζ-Tubulin
Zeta-tubulin (IPR004058) is present in many eukaryotes, but missing from others, including placental mammals. It has been shown to be associated with the basal foot structure of centrioles in multiciliated epithelial cells.[4]
Prokaryotic
BtubA/B
BtubA (Q8GCC5) and BtubB (Q8GCC1) are found in some bacterial species in the Verrucomicrobiota genus Prosthecobacter.[6] Their evolutionary relationship to eukaryotic tubulins is unclear, although they may have descended from a eukaryotic lineage by lateral gene transfer.[19][18] Compared to other bacterial homologs, they are much more similar to eukaryotic tubulins. In an assembled structure, BtubB acts like α-tubulin and BtubA acts like β-tubulin.[35]
FtsZ
Many bacterial and euryarchaeotal cells use FtsZ to divide via binary fission. All chloroplasts and some mitochondria, both organelles derived from endosymbiosis of bacteria, also use FtsZ.[36] It was the first prokaryotic cytoskeletal protein identified.
TubZ
TubZ (Q8KNP3; pBt156) was identified in Bacillus thuringiensis as essential for plasmid maintenance.[8] It binds to a DNA-binding protein called TubR (Q8KNP2; pBt157) to pull the plasmid around.[37]
CetZ
CetZ (D4GVD7) is found in the euryarchaeal clades of Methanomicrobia and Halobacteria, where it functions in cell shape differentiation.[10]
Phage tubulins
Phages of the genus Phikzlikevirus, as well as a Serratia phage PCH45, use a shell protein (Q8SDA8) to build a nucleus-like structure called the phage nucleus. This structure encloses DNA as well as replication and transcription machinery. It protects phage DNA from host defenses like restriction enzymes and type I CRISPR-Cas systems. A spindle-forming tubulin, variously named PhuZ (B3FK34) and gp187, centers the nucleus in the cell.[38][39]
Odinarchaeota tubulin
Asgard archaea tubulin from hydrothermal-living Odinarchaeota (OdinTubulin) was identified as a genuine tubulin. OdinTubulin forms protomers and protofilaments most similar to eukaryotic microtubules, yet assembles into ring systems more similar to FtsZ, indicating that OdinTubulin may represent an evolution intermediate between FtsZ and microtubule-forming tubulins.[40]
Pharmacology
Tubulins are targets for anticancer drugs[41][42][43] such as vinblastine and vincristine,[44][45] and paclitaxel.[46] The anti-worm drugs mebendazole and albendazole as well as the anti-gout agent colchicine bind to tubulin and inhibit microtubule formation. While the former ultimately lead to cell death in worms, the latter arrests neutrophil motility and decreases inflammation in humans. The anti-fungal drug griseofulvin targets microtubule formation and has applications in cancer treatment.
Post-translational modifications
When incorporated into microtubules, tubulin accumulates a number of post-translational modifications, many of which are unique to these proteins. These modifications include detyrosination, acetylation, polyglutamylation, polyglycylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, and palmitoylation. Tubulin is also prone to oxidative modification and aggregation during, for example, acute cellular injury.[47]
Nowadays there are many scientific investigations of the acetylation done in some microtubules, specially the one by α-tubulin N-acetyltransferase (ATAT1) which is being demonstrated to play an important role in many biological and molecular functions and, therefore, it is also associated with many human diseases, specially neurological diseases.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.