Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Epiglottal plosive
Consonantal sound represented by ⟨ʡ⟩ in IPA From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The epiglottal or pharyngeal plosive (or stop) is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʡ⟩.
Esling (2010) describes the sound covered by the term "epiglottal plosive" as an "active closure by the aryepiglottic pharyngeal stricture mechanism" – that is, a stop produced by the aryepiglottic folds within the pharynx.[1]
Remove ads
Features
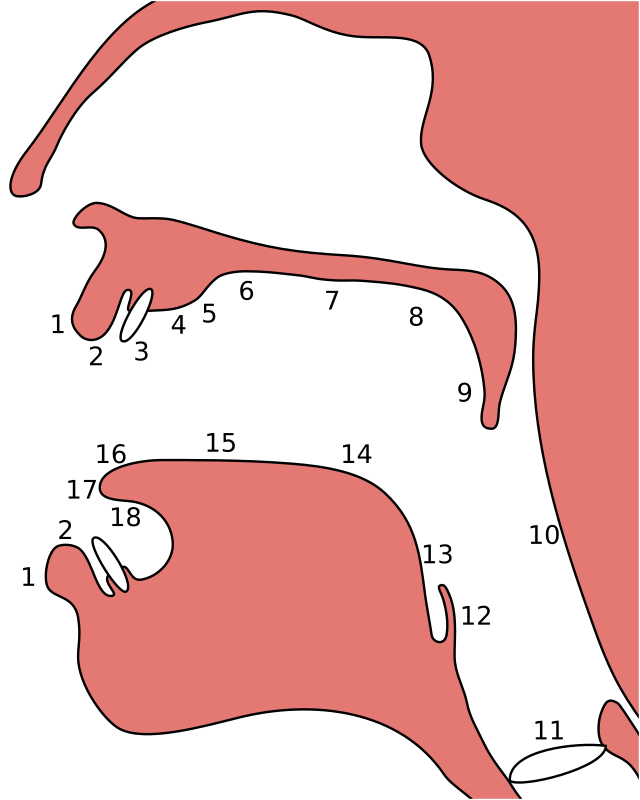
Features of the epiglottal stop:
- Its manner of articulation is occlusive, which means it is produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract. Since the consonant is also oral, with no nasal outlet, the airflow is blocked entirely, and the consonant is a plosive.
- Its place of articulation is epiglottal, which means it is articulated with the aryepiglottic folds against the epiglottis.
- It has no defined phonation, although it is typically voiceless, which means it is produced without vibrations of the vocal cords. Voiced epiglottal "stops" tend toward being epiglottal flaps.[citation needed]
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is exclusively allowed to escape through the mouth.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Remove ads
Occurrence
Remove ads
See also
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


