Muscles of the spine From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The transversospinales are a group of muscles of the human back. Their combined action is rotation and extension of the vertebral column. These muscles are small and have a poor mechanical advantage for contributing to motion. They include: the three semispinalis muscles, the multifidus muscle, and the rotatores muscles.
| Transversospinales | |
|---|---|
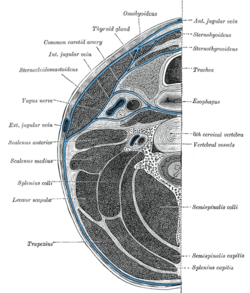 Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli. | |
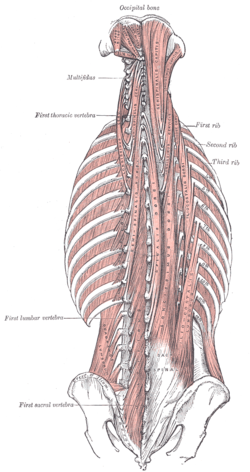 Deep muscles of the back. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Transverse process |
| Insertion | Spinous process |
| Nerve | Posterior ramus of spinal nerve |
| Actions | Extend vertebral column (bilateral contraction); rotate vertebral column (unilateral contraction) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculi transversospinales |
| TA98 | A04.3.02.201 |
| TA2 | 2275 |
| FMA | 71304 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The three semispinalis muscles, span 4-6 vertebral segments:
The multifidus muscle, and spans 2-4 vertebral segments
The rotatores muscles, lie beneath the multifidus, and spans 1-2 vertebral segments
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.