Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
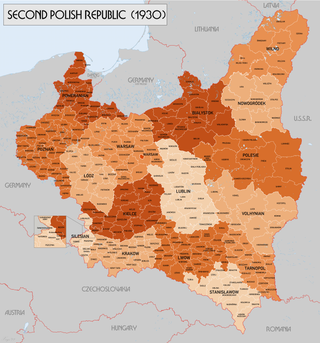
Subdivisions of the Second Polish Republic
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Subdivisions of the Second Polish Republic became an issue immediately after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in 1918. The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had been partitioned in the late 18th century. The various parts of what was now Polish territory had belonged to different states with different administrative structures: Austria-Hungary (mostly forming part of the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria), the German Empire (specifically the Kingdom of Prussia) and the Russian Empire.
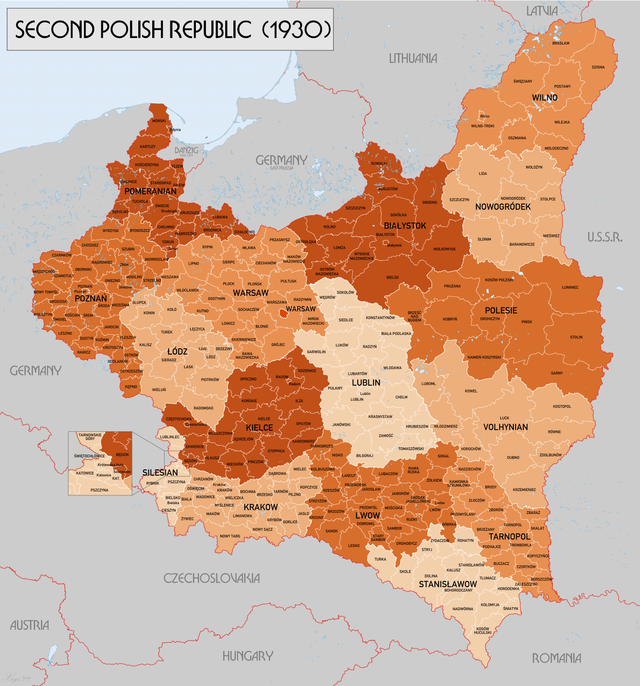


In 1919 the first voivodeships of interwar Poland were created; in addition, the capital of Warsaw had the status of an independent city-voivodeship. In the years 1919–1921 additional voivodeships were created, as borders of Poland were still fluid, with events such as the Silesian Uprisings in the West and the Polish-Soviet War in the East. Eventually by 1921 Poland would have 15 voivodeships, the Warsaw capital city-voivodeship and the Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship (the system known as 15+1+1). Additionally, the creation of the new Sandomierz Voivodeship was planned for late 1939.
The lower level of administration, below voivodeships, were powiats (counties). They were subject to several reforms, particularly in early and late 1930s. Below them were gminas and gromadas. Shortly before the Second World War, in April 1939, Poland had 264 powiats, 611 urban and 3195 rural gminas and 40533 gromads.
The division was based on a three-tier system. On the lowest rung were the gminy, which were little more than local town and village governments. These were then grouped together into powiaty which were then arranged into województwa.
On April 1, 1938, the borders of several western Voivodeships changed considerably. For more information, see Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938.
Remove ads
Polish Voivodeships 1919–1939
Total number of Voivodeships - 16, plus the capital city of Warsaw, which was regarded as a separate unit.
Biggest Voivodeships (as of August 1, 1939)
- Polesie Voivodeship - area 36,668 km2 (14,158 sq mi)
- Volhynian Voivodeship - area 35,754 km2 (13,805 sq mi)
- Warszawa Voivodeship - area 31,656 km2 (12,222 sq mi)
Smallest Voivodeships (as of August 1, 1939)
- miasto stołeczne Warszawa (the capital city of Warsaw) - area 141 km2 (54 sq mi)
- Silesian Voivodeship - area 5,122 km2 (1,978 sq mi)
- Tarnopol Voivodeship - area 16,533 km2 (6,383 sq mi)
Most populous Voivodeships
- Lwów Voivodeship - pop. 3 126 300,
- Kielce Voivodeship - pop. 2 671 000,
- Łódź Voivodeship - pop. 2 650 100.
Least populous Voivodeships
- Nowogródek Voivodeship - pop. 1 057 200,
- Polesie Voivodeship - pop. 1 132 200,
- miasto stołeczne Warszawa (the capital city of Warsaw) - pop. 1 179 500.
Remove ads
Polish Counties 1919–1939
Total number of counties (as of August 1, 1939) - 264, including 23 urban counties.
Biggest counties (as of August 1, 1939)
Smallest counties (as of August 1, 1939)
Most populous counties
Least populous counties
- city of Bielsko county, (pop. 25 400),
- city of Gniezno, (pop. 30 700),
- Międzychód county, (pop. 31 000).
Remove ads
Sources
- Mały rocznik statystyczny 1939, Nakładem Głównego Urzędu Statystycznego, Warszawa 1939 (Concise Statistical Year-Book of Poland, Warsaw 1939).
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads