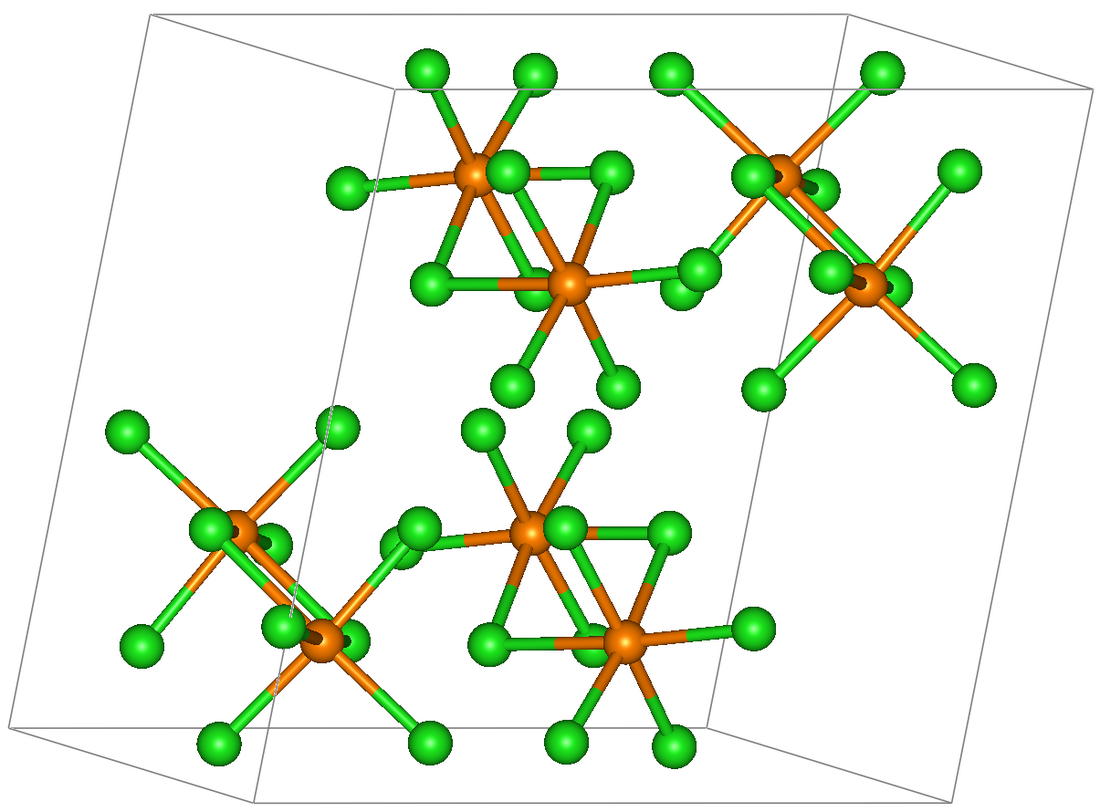
Rhenium pentachloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Re2Cl10. This red-brown solid[3] is paramagnetic.[4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Rhenium pentachloride | |
| Other names
Rhenium(V) chloride, Rhenium chloride, pentachlororhenium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.660 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| ReCl5 | |
| Molar mass | 363.471 g/mol |
| Appearance | red-brown |
| Density | 4.9 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K) |
| Boiling point | N/A |
| Will react to decompose and release HCl (g) | |
| +1225.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mP48; a = 0.924 nm, b = 1.154 nm, c = 1.203 nm, α = 90°, β = 109.1°, γ = 90° [1] | |
| P21/c, No. 14 | |
| Octahedral | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
releases HCl upon hydrolysis |
| GHS labelling:[2] | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Rhenium pentafluoride |
Other cations |
Osmium pentachloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Structure and preparation
Rhenium pentachloride has a bioctahedral structure and can be described as Cl4Re(μ-Cl)2ReCl4. The (μ-Cl)2 part of this formula indicates that two chloride ligands are bridging ligands, i.e. they connect to two Re atoms. The Re-Re distance is 3.74 Å.[1] The motif is similar to that seen for tantalum pentachloride.
This compound was first prepared in 1933,[5] a few years after the discovery of rhenium. The preparation involves chlorination of rhenium at temperatures up to 900 °C.[3] The material can be purified by sublimation.
ReCl5 is one of the most oxidized binary chlorides of Re. It does not undergo further chlorination. ReCl6 has been prepared from rhenium hexafluoride.[6] Rhenium heptafluoride is known but not the heptachloride.[7]
Uses and reactions
It degrades in air to a brown liquid.[8]
Although rhenium pentachloride has no commercial applications, it is of historic significance as one of the early catalysts for olefin metathesis.[9] Reduction gives trirhenium nonachloride.
Oxygenation affords the Re(VII) oxychloride:[10]
- ReCl5 + 3 Cl2O → ReO3Cl + 5 Cl2
Comproportionation of the penta- and trichloride gives rhenium tetrachloride.
References
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.