Loading AI tools
Regional Internet Registry representing Europe, the former USSR and West Asia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
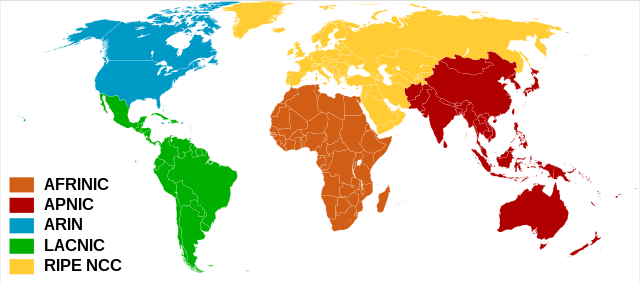
RIPE NCC (Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre) is the regional Internet registry (RIR) for Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Central Asia. Its headquarters are in Amsterdam, Netherlands, with a branch office in Dubai, UAE.[1]
 | |
| Founded | April 1992 |
|---|---|
| Focus | Allocation and registration of IP address space |
| Location |
|
| Website | www |
A RIR oversees the allocation and registration of Internet number resources (IPv4 addresses, IPv6 addresses and autonomous system numbers) in a specific region.
The RIPE NCC supports the technical and administrative coordination of the infrastructure of the Internet. It is a not-for-profit membership organisation with over 10,000 (as of March 2014[2]) members located in over 76 countries in its service region.[3]
Any individual or organisation can become a member of the RIPE NCC. The membership consists mainly of Internet service providers (ISPs), telecommunication organisations, educational institutions, governments, regulatory agencies, and large corporations.
The RIPE NCC also provides technical and administrative support to Réseaux IP Européens (RIPE), a forum open to all parties with an interest in the technical development of the Internet.
The RIPE NCC began its operations in April 1992 in Amsterdam, Netherlands. Initial funding was provided by the academic networks Réseaux Associés pour la Recherche Européenne (RARE) members, EARN, and EUnet. The RIPE NCC was formally established when the Dutch version of the Articles of Association was deposited with the Amsterdam Chamber of Commerce on 12 November 1997.[4] The first RIPE NCC Activity Plan[5] was published in May 1991.
On 25 November 2019, RIPE NCC announced[6] that it had made its “final /22 IPv4 allocation from the last remaining addresses in our available pool. We have now run out of IPv4 addresses.” RIPE NCC will continue to allocate IPv4 addresses, but only “from organisations that have gone out of business or are closed, or from networks that return addresses they no longer need. These addresses will be allocated to our members (LIRs) according to their position on a new waiting list ….” The announcement also called for support for the implementation of the IPv6 roll-out.

The RIPE NCC support technical coordination of the Internet infrastructure in its service region[7] and beyond. It undertakes many activities in this area, including:
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2018) |
The RIPE NCC is governed by Dutch law. Its legal form is a “vereniging” (association).
The RIPE NCC consists of:

Réseaux IP Européens is a forum open to all parties with an interest in the technical development of the Internet. Although similar in name, RIPE and the RIPE NCC are separate entities. However, they are highly interdependent. The RIPE NCC provides administrative support to RIPE, such as the facilitation of RIPE Meetings[21] and giving administrative support to RIPE Working Groups.[22]
The RIPE NCC charges members an annual membership fee.[23] Since 2012 this fee has been equal for all members and is unrelated to resource holdings. A separate charge is made for each Provider Independent number resource associated with customers of members.
There is also an active market in IPv4 address transfers[24] and these relate to registration in the RIRs' databases rather than the addresses themselves. The RIPE NCC has a formal transfer process.[25] Members must pay their annual fees before they can transfer resources away.[26]
The RIPE Database[16] is a public database containing registration details of the IP addresses and AS numbers originally allocated to members by the RIPE NCC. It shows which organisations or individuals currently hold which Internet number resources, when the allocations were made and contact details. The organisations or individuals that hold these resources are responsible for updating information in the database.
As of March 2008, the database contents are available for near real-time mirroring (NRTM).[27]
The RIPE Routing Registry (RR)[28] is a sub-set of the RIPE Database[16] and holds routing information in RPSL. The RIPE RR[28] is a part of the Internet RR, a collection of databases that mirror each other. Information about domain names in the RIPE Database[16] is for reference only. It is not the domain name registry that is run by the country code Top Level Domain (ccTLD) administrators of Europe and surrounding areas.
The RIPE NCC service region[3] consists of countries in Europe, the Middle East and parts of Central Asia. RIPE NCC services are available to users outside this region through Local Internet Registries; these entities must have a valid legal address inside the service region but can offer their services to anyone.[7]
Prior to the formation of AFRINIC, the RIPE NCC served the following countries:[32]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.