Loading AI tools
Oceanic trench on a transform boundary between the Caribbean and North American plates From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Puerto Rico Trench is located on the boundary between the North Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea, parallel to and north of Puerto Rico, where the oceanic trench reaches the deepest points in the Atlantic Ocean. The trench is associated with a complex transition from the Lesser Antilles frontal subduction zone between the South American plate and Caribbean plate to the oblique subduction zone and the strike-slip transform fault zone between the North American plate and Caribbean plate, which extends from the Puerto Rico Trench at the Puerto Rico–Virgin Islands microplate through the Cayman Trough at the Gonâve microplate to the Middle America Trench at the Cocos plate.[1][2][3][4][5][6]

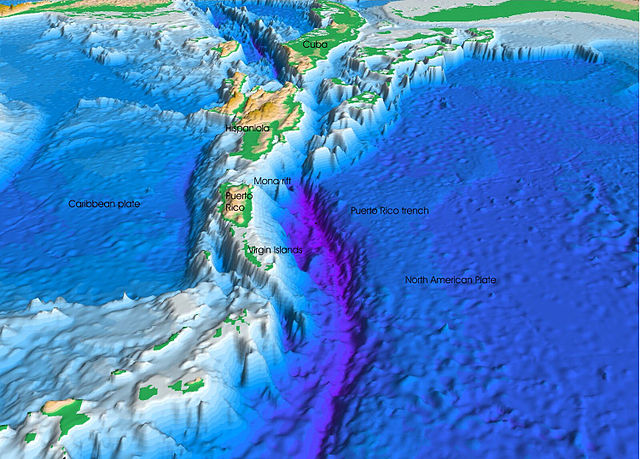
Constituting the deepest points in the Atlantic Ocean, the trench is 810 kilometres (503 mi) long[7] and has a maximum documented depth between 8,376 metres (27,480 ft)[8] and 8,740 metres (28,675 ft).[7][9] The deepest point is commonly referred to as the Milwaukee Deep, with the Brownson Deep naming the seabed surrounding it.[10] However, more recently, the latter term has also been used interchangeably with the former to refer to this point.[11][12][13] The exact point was identified by the DSSV Pressure Drop using a state-of-the-art Kongsberg EM124 multibeam sonar in 2018, and then directly visited and its depth verified by the crewed submersible Deep-Submergence Vehicle DSV Limiting Factor (a Triton 36000/2 model submersible) piloted by Victor Vescovo.[14][15][16]
Scientific studies have concluded that an earthquake occurring along this fault zone could generate a significant tsunami.[17] The island of Puerto Rico, which lies immediately to the south of the fault zone and the trench, suffered a destructive tsunami soon after the 1918 San Fermín earthquake.
The Puerto Rico Trench is located at a boundary between two plates that pass each other along a transform boundary with only a small component of subduction. The Caribbean plate is moving to the east relative to the North American plate. The North American plate is being subducted by the Caribbean plate obliquely at the trench while to the southeast, the South American plate is being more directly subducted along the Lesser Antilles subduction zone. This subduction zone explains the presence of active volcanoes over the southeastern part of the Caribbean Sea. Volcanic activity is frequent along the Lesser Antilles island arc southeast from Puerto Rico to the northern coast of South America.
Although originally part of a volcanic arc, the Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico, Hispaniola, Cuba, and Jamaica do not have active volcanoes. The Virigin Islands and Puerto Rico do not have active volcanic activity since approximately 30 million years ago,[18] while the last active volcanoes in Hispaniola, Thomazanue and Morne la Vigie, became extinct within 1.5 million years ago. However, the islands are at risk of earthquakes and tsunamis. The Puerto Rico Trench has produced earthquakes greater than magnitude 8.0 and is considered capable of continuing to do so.[19][20]
According to NASA, beneath the trench is a mass so dense it deflects gravitational pull on the surface of the ocean, causing it to dip somewhat. It also has a negative effect on the accuracy of navigational instruments.[21]
Knowledge of the earthquake and tsunami risks has not been widespread among the general public of the islands located near the trench. Since 1988, the Puerto Rican Seismic Society has been trying to use the Puerto Rican media to inform people about a future earthquake that could result in a catastrophic tragedy.
Following the 2004 tsunami that affected more than forty countries in the Indian Ocean, many more people now fear the consequences that such an event would bring to the Caribbean. Local governments have begun emergency planning. In the case of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, the United States government has been studying the problem for years.[22] It is increasing its seismic investigations and developing tsunami warning systems.

On 11 October 1918, the western coast of Puerto Rico was hit by a major earthquake which caused a tsunami. The 1918 earthquake was caused by an old left-lateral strike-slip fault near the Mona Passage. In 1953, Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic, was affected by the Santo Domingo earthquake. The actual subduction zone (Puerto Rico Trench) has not ruptured in over 200 years, which is a major concern to geophysicists, as they believe it may be due for a major event.
Puerto Rico has always been an area of concern to earthquake experts because, apart from the 1918 episode, there are frequent tremors in and around the island, indicating activity. A 1981 tremor was felt across the island, while another in 1985 was felt in the towns of Cayey and Salinas.
The January 13, 2014 M 6.4 earthquake north of Puerto Rico occurred as a result of oblique-thrust faulting. Preliminary faulting mechanisms for the event indicate it ruptured either a structure dipping shallowly to the south and striking approximately east-west, or a near-vertical structure striking northwest-southeast. At the location of this earthquake, the North America plate moves west-southwest with respect to the Caribbean plate at a velocity of approximately 20 mm/yr, and subducts beneath the Caribbean plate at the Puerto Rico Trench. The location, depth and mechanism of the earthquake are consistent with the event occurring on this subduction zone interface."[23]
| Location[22] | Year | M |
|---|---|---|
| Puerto Rico Trench | 8.1 | |
| Anegada Trough | 7.5 | |
| Mona Canyon | 1918 | 7.5 |
| Mona Canyon | 1943 | 7.5 |
| Dominican Republic | 8.1 | |
| Dominican Republic | 1953 | 6.9 |
| Puerto Rico Trench | 2014 | 6.4 |
| Puerto Rico Trench | 2019 | 6.0 |
| Muertos Trough | 6.4 |
Several exploration cruises carried out by USGS in the Puerto Rico Trench have for the first time mapped the entire trench using ship mounted multibeam bathymetry.
The seafloor was visited for the first time by French bathyscaphe Archimède in 1964[24][25] and then by a robotic vehicle in 2012.[26] The most conspicuous aspect of the footage was the swarm of benthic amphipods. Some of these amphipods were collected by bait bags attached to the vehicle and were brought to the surface for further analysis. The samples recovered were Scopelocheirus schellenbergi, a species of lysianassid amphipod that have so far only been found in ultradeep trenches in the Pacific.[27]
Two invertebrate creatures were also observed in the video. One soft dark individual, estimated to be 10–20 cm (3.9–7.9 in) long, has been identified by Dr. Stace E. Beaulieu of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution as a sea cucumber, tentatively assigned to genus Peniagone. The other individual, a small crustacean, is tentatively identified as a munnopsid isopod, based on morphology and similar walking and jumping movements observed for other hadal munnopsid isopods. Because these individuals were not collected, it is not possible to obtain species-level identifications. However, these sightings likely exceed the deepest known records for genus Peniagone and family Munnopsidae.

The American explorer Victor Vescovo dived to the deepest point of the Puerto Rico Trench and therefore the Atlantic Ocean on 19 December 2018, as part of the Five Deeps Expedition. He reached a depth of 8,376 m (27,480 ft) ±5 m (16 ft) at 19°42'49" N, 67°18'39" W by direct CTD pressure measurements with the Deep-Submergence Vehicle DSV Limiting Factor (a Triton 36000/2 model submersible) and thus became the first person to reach the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean while also making the second-deepest recorded solo dive in history at that time.[28] Many media outlets referred to the deep as Brownson Deep,[11][12][13] in opposition to past references to the area, where the term Milwaukee Deep was used instead.
The operating area was surveyed by the support ship, the Deep Submersible Support Vessel DSSV Pressure Drop, with a Kongsberg SIMRAD EM124 multibeam echosounder system. The gathered data will be donated to the GEBCO Seabed 2030 initiative.[29][30] The dive was part of the Five Deeps Expedition. The objective of this expedition was to thoroughly map and visit the deepest points of all five of the world's oceans by the end of September 2019.[31][32]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.