Lambdoid suture
Connective tissue between the parietal bones and the occipital bone of the skull From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The lambdoid suture, or lambdoidal suture, is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture.
| Lambdoid suture | |
|---|---|
 Lambdoid suture, posterior view | |
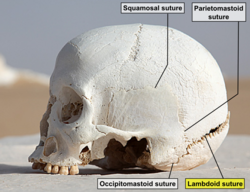 Lambdoid suture (labeled at bottom right) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Skull |
| Nerve | Supraorbital nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sutura lambdoidea |
| TA98 | A03.1.02.004 |
| TA2 | 1577 |
| FMA | 52933 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Structure
The lambdoid suture is between the paired parietal bones and the occipital bone of the skull. It runs from the asterion on each side.
Nerve supply
The lambdoid suture may be supplied by a branch of the supraorbital nerve, a branch of the frontal branch of the trigeminal nerve.[1][2]
Clinical significance
At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. If certain bones of the skull grow too fast, then craniosynostosis (premature closure of the sutures) may occur. This can result in skull deformities. If the lambdoid suture closes too soon on one side, the skull will appear twisted and asymmetrical, a condition called "plagiocephaly". Plagiocephaly refers to the shape and not the condition. The condition is craniosynostosis.[citation needed]
Etymology
The lambdoid suture is named due to its uppercase lambda-like shape.
Additional images
- Animation. Lambdoid suture shown in red.
- Parietal bones (above) and occipital bone (below).
- Lambdoid suture seen from above.
- Lambdoid suture seen from inside.
- Lambdoid suture, medial view. Indicated by yellow line.
- Lambdoid suture with Wormian bones, seen from behind.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.






