Loading AI tools
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of flags in the United States describing the evolution of the flag of the United States, as well as other flags used within the United States, such as the flags of governmental agencies. There are also separate flags for embassies and ships.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2019) |
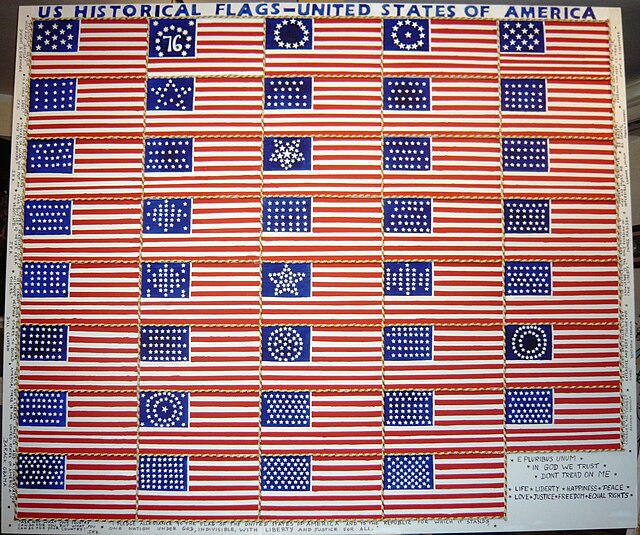
Since 1818, a star for each new state has been added to the flag on the Fourth of July the year immediately following each state's admission. In years in which multiple states have been admitted, the corresponding number of stars were added to the flag. This change has typically been the only change made with each revision of the flag since 1777, with the exception of changes in 1795 and 1818, which increased the number of stripes to 15 and then returned it to 13, respectively. As the exact pattern of stars was not specified prior to 1912, many of the historical U.S. national flags (shown below) have had varied arrangements of the stars.[1]
![]() Flag of the Chief of Naval Operations
Flag of the Chief of Naval Operations
![]() Flag of the Vice Chief of Naval Operations
Flag of the Vice Chief of Naval Operations
![]() Flag of the Navy fleet admiral
Flag of the Navy fleet admiral
![]() Flag of an unrestricted line (URL) Navy admiral (staff corps flag officers have white flags with the appropriate number of blue stars in an identical pattern as URL admiral's flags).
Flag of an unrestricted line (URL) Navy admiral (staff corps flag officers have white flags with the appropriate number of blue stars in an identical pattern as URL admiral's flags).
![]() Flag of an URL Navy vice admiral
Flag of an URL Navy vice admiral
![]() Flag of an URL Navy rear admiral
Flag of an URL Navy rear admiral
![]() Flag of an URL Navy rear admiral (lower half)
Flag of an URL Navy rear admiral (lower half)
![]() Flag of Military Sealift Command
Flag of Military Sealift Command
The Civil Air Patrol (CAP) is a congressionally chartered, federally supported non-profit corporation that serves as the official civilian auxiliary of the U.S. Air Force. It has quasi-military organizational and rank structures modeled on those of the Air Force.[2]
![]() Flag of the Department of the Interior
Flag of the Department of the Interior
![]() Flag of the Secretary of the Interior
Flag of the Secretary of the Interior
![]() Flag of the Deputy Secretary of the Interior
Flag of the Deputy Secretary of the Interior
![]() Flag of the National Park Service
Flag of the National Park Service
![]() Guidon of the National Park Service
Guidon of the National Park Service
![]() Flag of the Bureau of Indian Affairs
Flag of the Bureau of Indian Affairs
![]() Flag of the Fish and Wildlife Service
Flag of the Fish and Wildlife Service
![]() Flag of the Bureau of Land Management
Flag of the Bureau of Land Management
![]() Flag of the Geological Survey
Flag of the Geological Survey
Many agencies, departments, and offices of the U.S. federal government have their own flags, guidons, or standards. Following traditional American vexillology, these usually consist of the agency's departmental seal on a blank opaque background, but not always.

The flags of the U.S. states, territories, and federal district exhibit a variety of regional influences and local histories, as well as different styles and design principles. Nonetheless, the majority of the states' flags share the same design pattern consisting of the state seal superimposed on a monochrome background, commonly every different shade of blue, which remains a source of criticism from vexillologists.
The most recent current state flag is that of Minnesota (May 11, 2024), while the most recent current territorial flag is that of the Northern Mariana Islands (July 1, 1985).
Modern U.S. state flags date from the 1890s, when states wanted to have distinctive symbols at the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago, Illinois. Most U.S. state flags were designed and adopted between 1893 and World War I.[3]
According to a 2001 survey by the North American Vexillological Association, New Mexico has the best-designed flag of any U.S. state, U.S. territory, or Canadian province, while Georgia's state flag was rated the worst design.[4] (Georgia adopted a new flag in 2003; Nebraska's state flag, whose design was rated second worst, remains in use to date.)
Dates in parentheses denote when the current flag was adopted by the state's legislature.
Flag of California
(February 3, 1911)
Flag of Connecticut
(September 9, 1897)
Flag of Massachusetts
(July 3, 1971)
Flag of Mississippi
(January 11, 2021)
Flag of New Hampshire
(1931)
Flag of New Jersey
(May 11, 1896)
Flag of New Mexico
(March 15, 1925)
Flag of North Carolina
(March 9, 1885)[7]
Flag of North Dakota
(March 11, 1911)
Flag of Pennsylvania
(June 13, 1907)
Flag of Rhode Island
(November 1, 1897)
Flag of South Carolina
(January 26, 1861)
Flag of South Dakota
(November 9, 1992)
Flag of Washington
(March 5, 1923)
Flag of West Virginia
(March 7, 1929)
Since 1777, the national ensign of the United States has also simultaneously served as its national flag. The current version is shown below; for previous versions, please see the section Historical progression of designs above.
While the countries mentioned are recognized independent nations with United Nations seats, the United States maintains and exercises jurisdictional control over the countries in defense, security, and funding grants.
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
![]() Flag of the President (1882)
Flag of the President (1882)
![]() Flag of the President (1899)
Flag of the President (1899)
![]() Flag of the President (1902)
Flag of the President (1902)
![]() Flag of the President (1916)
Flag of the President (1916)
![]() Flag of the President (1945)
Flag of the President (1945)
![]() Flag of the Vice President (1915)
Flag of the Vice President (1915)
![]() Flag of the Vice President (1936)
Flag of the Vice President (1936)
![]() Flag of the Vice President (1948)
Flag of the Vice President (1948)
![]() Flag of the Environmental Science Services Administration (1965–1970)
Flag of the Environmental Science Services Administration (1965–1970)
![]() Flag of the Federal Emergency Management Agency (until 2003)
Flag of the Federal Emergency Management Agency (until 2003)
![]() Flag of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (until 2003)
Flag of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (until 2003)
![]() Flag of the Immigration and Naturalization Service
Flag of the Immigration and Naturalization Service
![]() Flag of the Department of the Interior (until 1917)
Flag of the Department of the Interior (until 1917)
Flag of the General Services Administration (1972–1973)
Flag of the General Services Administration (1973–1989)
![]() Flag of the Secretary of the Interior (1917–1934)
Flag of the Secretary of the Interior (1917–1934)
![]() Infantry Battalion flag (de facto flag of the U.S. Navy until 1959)
Infantry Battalion flag (de facto flag of the U.S. Navy until 1959)
![]() Flag of the Secretary of Labor (1915–1960)
Flag of the Secretary of Labor (1915–1960)
![]() Flag of the Department of Labor (1915–1960)
Flag of the Department of Labor (1915–1960)
![]() Flag of the Secretary of the Treasury (1887–1915)
Flag of the Secretary of the Treasury (1887–1915)
![]() Flag of the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare
Flag of the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare
![]() Flag of the Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare
Flag of the Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare
![]() Flag of the Public Health and Marine-Hospital Service
Flag of the Public Health and Marine-Hospital Service
![]() Flag of the Marine Hospital Service
Flag of the Marine Hospital Service
![]() Flag of the Bureau of Navigation (?–1946)
Flag of the Bureau of Navigation (?–1946)
![]() Flag of the Director of the Bureau of Marine Inspection and Navigation (?–1946)
Flag of the Director of the Bureau of Marine Inspection and Navigation (?–1946)
![]() Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1799)
Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1799)
![]() Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1815)
Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1815)
![]() Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1836)
Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1836)
![]() Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1841)
Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1841)
![]() Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1867)
Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1867)
![]() Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1868)
Ensign of the Revenue-Marine (1868)
![]() Ensign of the Coast Guard (1915–1953)
Ensign of the Coast Guard (1915–1953)
![]() Flag of the Coast Guard Auxiliary (1940–1968)
Flag of the Coast Guard Auxiliary (1940–1968)
![]() Flag of the Office of Homeland Security (2001–2002)
Flag of the Office of Homeland Security (2001–2002)
![]() Flag of the Director of Central Intelligence
Flag of the Director of Central Intelligence
![]() Flag of the National Imagery and Mapping Agency
Flag of the National Imagery and Mapping Agency
![]() Flag of U.S. Forces – Iraq (2010–2011)
Flag of U.S. Forces – Iraq (2010–2011)
![]() Flag of the United States Bureau of Fisheries (?–1940)
Flag of the United States Bureau of Fisheries (?–1940)
![]() Flag of the Commissioner of Fisheries (?–1940)
Flag of the Commissioner of Fisheries (?–1940)
![]() Flag of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey (1899–1970)
Flag of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey (1899–1970)
Commissioning pennant of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey for Class I vessels ( ? –1970)
Commissioning pennant of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey for Class II, III, and IV vessels ( ? –1970)
![]() Pennant of the
Pennant of the
United States Life-Saving Service
(?–1915)
![]() Pennant of the United States Lighthouse Service
Pennant of the United States Lighthouse Service
(?–1939)
![]() Flag of the Commissioner of Lighthouses
Flag of the Commissioner of Lighthouses
(?–1939)
![]() Flag of the Superintendent of Lighthouses
Flag of the Superintendent of Lighthouses
(?–1939)
![]() Flag of the Marine Corps
Flag of the Marine Corps
(1914–1939)
![]() Flag of the Chief of Chaplains of the United States Army
Flag of the Chief of Chaplains of the United States Army
![]() Flag of the United States Army Adjutant General's Corps
Flag of the United States Army Adjutant General's Corps
![]() Flag of the United States Army Chaplain Corps (1983-1993)
Flag of the United States Army Chaplain Corps (1983-1993)
![]() Flag of the 140th Military Intelligence Battalion
Flag of the 140th Military Intelligence Battalion
![]() Fort Sumter Flag (1861)
Fort Sumter Flag (1861)
![]() Flag of the Chief of the National Guard Bureau (1998-2008)
Flag of the Chief of the National Guard Bureau (1998-2008)
![]() Flag of the Department of Transportation (1967–1980)
Flag of the Department of Transportation (1967–1980)
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.