Loading AI tools
Bilateral relations From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
China–Netherlands relations officially began in November 1954.[1] In May 1972, diplomatic mission was increased to ambassadorial level.[1] On 11 May 1981, the diplomatic relations was downgraded to the charge d'affaires level due to the Dutch government ratified the construction of two submarines for Taiwan by the Dutch companies. Until 1 February 1984, China and the Netherlands restored ambassadorial diplomatic relations.[1]
 | |
China |
Netherlands |
|---|---|

China-Dutch relations began prior to the founding of the People's Republic of China in the 17th and 18th century when Dutch traders of the Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie (VOC) setup trading post in Canton and also in the western coast of Taiwan.[2] Johan Nieuhof's account of the first VOC embassy to Beijing in 1655–1657—and the objections against it raised by members of the Jesuit China Mission—became the influential and much-translated 1665 Embassy from the East-India Company.
PRC–Netherlands began in 1954 to establish the diplomatic relations of the charge d'affaires level. Until 18 May 1972, China upgraded to the ambassadorial level with the Netherlands.[3] In the 1980s Taiwan ordered two submarines from a Dutch shipyard which were delivered despite tremendous Chinese pressure.[4] China accused the Netherlands of colluding with American President Ronald Reagan and downgraded relations to the charge d'affaires level with the Netherlands on 11 May 1981, and threatened to do the same to the US.[5] In 1984, the Netherlands agreed not to export additional military goods in order to restore relations to the ambassadorial level.[6]
Netherlands export to China includes petrochemicals, machinery, transport equipment, food, high technology and fossil fuels.[7] China's export to the Netherlands includes computer and consumer electronics, toys and clothes.[7][8][9]
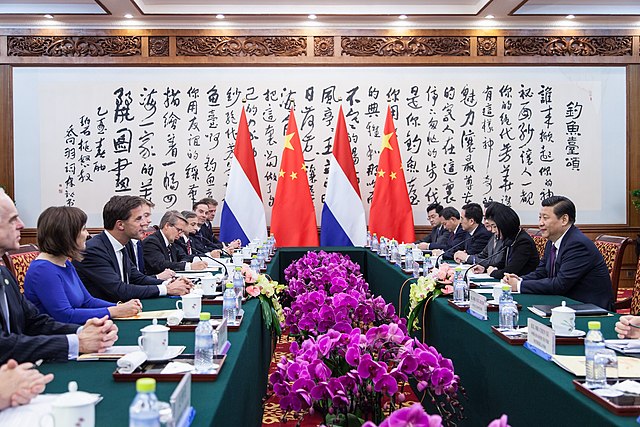
In March 2014, Chinese Communist Party general secretary Xi Jinping made the first state visit of China to the Netherlands in history.[10]
In July 2019, the UN ambassadors from 22 nations, including Netherlands, signed a joint letter to the UNHRC condemning China's mistreatment of the Uyghurs as well as its mistreatment of other minority groups, urging the Chinese government to close the Xinjiang internment camps.[11][12]
In February 2021, the Dutch House of Representatives voted to recognize the Chinese government's treatment of its Uyghur Muslim minority as genocide, becoming the first country in the European Union to do so.[13]
In February 2024, the Dutch Military Intelligence and Security Service and the General Intelligence and Security Service stated that Chinese state hackers penetrated a Dutch military network the prior year.[14] The same month, Dutch trade minister Geoffrey van Leeuwen justified export controls on ASML tools to China on the grounds that they would be used for "high-value weapons systems and weapons of mass destruction."[15] In April 2024, the Dutch Military Intelligence and Security Service stated that Chinese spies were actively targeting the Netherlands' semiconductor, aerospace and maritime industries in order to strengthen China's armed forces.[16]
In June 2024, the Dutch Ministry of Defence accused China of creating an "unsafe situation" when its fighter jets encircled Dutch frigate HNLMS Tromp in international waters in the East China Sea.[17][18] In October 2024, the Dutch National Coordinator for Security and Counterterrorism stated that Chinese state-backed cyberattacks had increasingly moved from cyberespionage to also prepare for sabotage.[19]

Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.