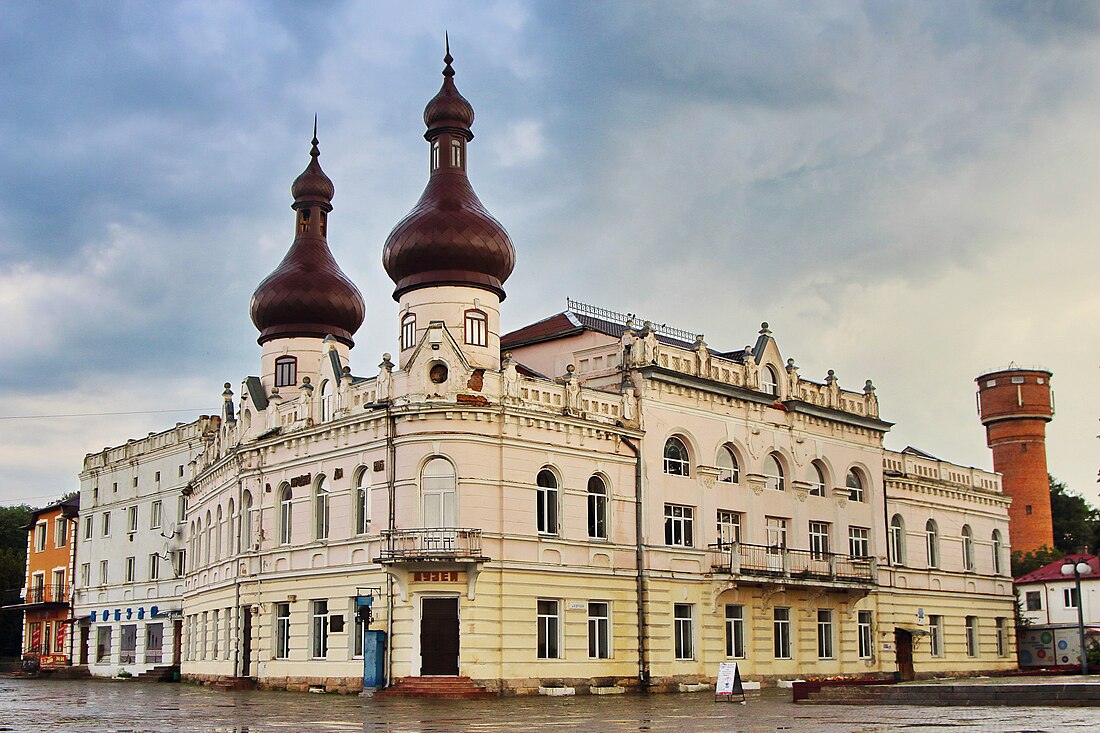
Borshchiv
City in Ternopil Oblast, Ukraine From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Borshchiv (Ukrainian: Борщів; Polish: Borszczów; Yiddish: בארשטשיוו, romanized: Borshtshev) is a city in Chortkiv Raion, Ternopil Oblast, western Ukraine. It was previously the administrative center of the former Borshchiv Raion until 2020. Borshchiv hosts the administration of Borshchiv urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine.[1] In 2022, the population was estimated to be 10,632.[2]
Borshchiv
Борщів Borszczów | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates: 48°48′10″N 26°2′11″E | |
| Country | |
| Oblast | Ternopil Oblast |
| Raion | Chortkiv Raion |
| Hromada | Borshchiv urban hromada |
| First mention | 1456 |
| Magdeburg Rights | 1629 |
| Population (2022) | |
| • Total | 10,632 |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |

History
Early history
Borshchiv has been mentioned under its name as the Dudinski family manor since 1456. In 1629 the town, which at that time belonged to the Kingdom of Poland was granted a Magdeburg charter, and the coat of arms, which was the symbol of the House of Vasa. In 1672–1683 the town was controlled by Ottoman Turks (see Polish–Ottoman War (1672–76)) as part of Podolia Eyalet. It was nominally ruled by Ottomans between 1683-1699 and ravaged by Poles and Turks in this period. After the Treaty of Karlowitz, it was returned to Poland. After the First Partition of Poland (1772), the town was annexed by the Habsburg Empire. In 1809–1815 it was controlled by the Russian Empire and then returned to Austrians.
20th century
In 1914–1917 it was taken over by the Russian troops again, see Russian occupation of Eastern Galicia, 1914–15. From 1919 to September 1939 it belonged to Poland, and due to proximity of the Polish-Soviet border, a Border Protection Corps Battalion Borszczow was stationed here. In the Second Polish Republic, Borszczow was the seat of a county (powiat) in Tarnopol Voivodeship.
During World War II, in September 1939, the town was annexed by the Soviet Union. A local newspaper is published here since October 1939.[3]
It was also occupied by the Axis troops in July 1941 and several mass executions of Jews were carried out in the town. In April 1942 a Borshchiv Jewish ghetto was established here. Between spring and summer of 1943, approximately 400 Jews were sent to the Ivanovka camp and more than 2,300 Jews were shot in the Jewish cemetery.[4]
In 1968 the population was 8600 people, there was a sugar factory, a dairy plant, а tobacco factory and distillery.[5]
In January 1989 the population was 11 306 people,[6] there was a sugar factory, a cheese factory,[7] а tobacco factory and distillery.[8]
21st century
Until 18 July 2020, Borshchiv served as the administrative center of Borshchiv Raion. The raion was abolished in July 2020 as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Ternopil Oblast to three. The area of Borshchiv Raion was merged into Chortkiv Raion.[9][10]
Geography
Geology
The Borshov Horizon or Borshovian Horizon is a geological layer of marl and limestone formed in the lowermost Devonian period.[11] Typical specimens of this province have been recorded in the Upper Dniester valleys near Borshchiv where it reaches the surface layers of the land. It is marked by the presence of microscopic Margachitina chitinozoans,[11] certain trilobites and bryozoa dispersed in grainstone. According to Pushkin, waterborne Bryozoa living in shallow lagoons were the dominant life form that shaped the Borschovian plains. Some areas of the Borschovian layer were dominated by colonies of a single species where others were populated by a mix of different Bryozoa.[12]
Climate
| Climate data for Borshchiv | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −0.7 (30.7) |
1.4 (34.5) |
7.1 (44.8) |
14.6 (58.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
23.4 (74.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
19.6 (67.3) |
12.9 (55.2) |
6.8 (44.2) |
1.4 (34.5) |
13.1 (55.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
2.8 (37.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
15.4 (59.7) |
18.9 (66.0) |
20.8 (69.4) |
20.2 (68.4) |
15.3 (59.5) |
9 (48) |
4 (39) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
9.2 (48.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −6.1 (21.0) |
−5 (23) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
4.5 (40.1) |
10 (50) |
13.9 (57.0) |
15.9 (60.6) |
15.4 (59.7) |
11 (52) |
5.4 (41.7) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
5.1 (41.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34 (1.3) |
38 (1.5) |
46 (1.8) |
57 (2.2) |
71 (2.8) |
92 (3.6) |
104 (4.1) |
70 (2.8) |
65 (2.6) |
46 (1.8) |
42 (1.7) |
40 (1.6) |
705 (27.8) |
| Average rainy days (≥ mm) | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 91 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83 | 81 | 74 | 66 | 63 | 65 | 67 | 66 | 68 | 76 | 83 | 82 | 73 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 2.6 | 3.4 | 5.9 | 8.9 | 10.6 | 11.1 | 11.3 | 10.2 | 7.8 | 5.4 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 6.9 |
| Source: Climate Data[13] | |||||||||||||
Monuments
Notable people
- Bolesław Bronisław Duch (1896–1980), Polish Major General
- Artur Dumanyuk (born 1996), Ukrainian professional footballer
- Oleksii Hunovskyi (1882–1961), Ukrainian Greek Catholic priest, composer, public figure, educator, political prisoner, and head of the Chortkiv District National Council of the ZUNR
- Bohdan Sehin (born 1976), Ukrainian composer, and organizer of music programs
- Vasyl Vyrozub (born 1970), Ukrainian priest and chaplain
References
External links
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.