Loading AI tools
Foodborne illness outbreak From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A novel strain of Escherichia coli O104:H4 bacteria caused a serious outbreak of foodborne illness focused in northern Germany in May through June 2011. The illness was characterized by bloody diarrhea, with a high frequency of serious complications, including hemolytic–uremic syndrome (HUS), a condition that requires urgent treatment. The outbreak was originally thought to have been caused by an enterohemorrhagic (EHEC) strain of E. coli, but it was later shown to have been caused by an enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC) strain that had acquired the genes to produce Shiga toxins, present in organic fenugreek sprouts.
| 2011 Germany E. coli O104:H4 outbreak | |
|---|---|
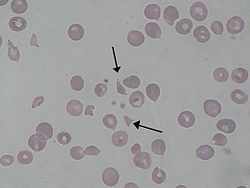 Schistocytes seen in a person with hemolytic-uremic syndrome | |
 Map of cases and restrictions in relation to the outbreak (click for key and enlarged version) | |
| Bacteria strain | Escherichia coli O104:H4 |
| Source | Contaminated organic fenugreek sprouts |
| Location | Western and Northern Europe, the United States and Canada |
| First outbreak | Aachen, Germany |
| Date | 1 May–21 July 2011 |
| Confirmed cases | 3,950 |
| Severe cases | 800 |
Deaths | 53 |
Epidemiological fieldwork suggested fresh vegetables were the source of infection. The agriculture minister of Lower Saxony identified an organic farm[1] in Bienenbüttel, Lower Saxony, Germany, which produces a variety of sprouted foods, as the likely source of the E. coli outbreak.[2] The farm was shut down.[2] Although laboratories in Lower Saxony did not detect the bacterium in produce, a laboratory in North Rhine-Westphalia later found the outbreak strain in a discarded package of sprouts from the suspect farm.[3] A control investigation confirmed the farm as the source of the outbreak.[4] On 30 June 2011, the German Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung (BfR) (Federal Institute for Risk Assessment), an institute of the German Federal Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Consumer Protection, announced that seeds of organic[5] fenugreek imported from Egypt were likely the source of the outbreak.[6]
In all, 3,950 people were affected and 53 died, 51 of whom were in Germany.[7] 800 people suffered hemolytic–uremic syndrome (HUS), which can lead to kidney failure.[8] A handful of cases were reported in several other countries including Switzerland,[9] Poland,[9] the Netherlands,[9] Sweden,[9] Denmark,[9] the UK,[9][10] Canada and the USA.[11] Essentially all affected people had been in Germany or France shortly before becoming ill.
Initially, German officials made incorrect statements on the likely origin and strain of Escherichia coli.[12][13][14][15] The German health authorities, without results of ongoing tests, incorrectly linked the O104 serotype to cucumbers imported from Spain.[16] Later, they recognised that Spanish greenhouses were not the source of the E. coli and cucumber samples did not contain the specific E. coli variant causing the outbreak.[17][18] Spain consequently expressed anger about having its produce linked with the deadly E. coli outbreak, which cost Spanish exporters US$200 million per week.[19] Russia banned the import of all fresh vegetables from the European Union from early June until 22 June 2011.[20]
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli has been linked to foodborne outbreaks of bloody diarrhea and hemolytic–uremic syndrome around the world since at least the early 1980s.[21] The majority of disease has been attributed to E. coli with the serotype O157:H7; however, over 100 E. coli serotypes have been associated with human diarrheal disease.[22]
In the five years before the outbreak (2006 to 2010) Germany experienced an average of 218 cases of EHEC gastroenteritis and 13 cases of hemolytic–uremic syndrome each year.[23] According to the German National Reference Centre for Salmonella and Other Enteric Pathogens, the most common serotypes in those years were O157, O26, O103, and O91.[24] Serotype O104 was relatively rare in Europe in the years preceding the outbreak, with just 11 reported cases in the EU and Norway between 2004 and 2009.[25]
Cases began as early as 1 May 2011 with a man in Aachen reporting bloody diarrhea.[23] Cases then rapidly increased, with over 100 cases of EHEC gastroenteritis and/or HUS were being reported each day by 16 May.[23] The outbreak centered on the five northern German states of Hamburg, Schleswig-Holstein, Bremen, Lower Saxony, and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.[23] Cases would eventually be reported in all 16 German states; however most cases outside of the northern states were linked to travel in northern Germany.[26] Additionally, a small number of cases were reported from other countries, although most of those ill had previously travelled to Germany. The most substantial outbreak outside of Germany was in Bordeaux, France where 15 cases of EHEC gastroenteritis were associated with the same strain of E. coli which caused the outbreak in Germany. The French cases had not previously travelled to Germany, suggesting they acquired the bacteria from contaminated sprouts grown in France.[23] Cases of EHEC HUS and gastroenteritis peaked on 21 and 22 May respectively.[26] Cases then slowly decreased over the following month, with cases reported throughout the month of June and ending during July 2011. German authorities deemed the outbreak over in early July 2011.[23]
The outbreak disproportionately affected adults and the elderly. 88% of hemolytic–uremic syndrome patients were over 17 years of age, and the median age of hemolytic–uremic syndrome patients was 42 years.[26] The median age of patients who died of gastroenteritis was 82 years, while the median age of patients who died from hemolytic–uremic syndrome was 74 years.[26]
Most or all victims were believed to have become infected in Germany or France. Confirmed cases are listed below according to their location when diagnosed.
| Country | Non-HUS cases | HUS cases | Deaths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Canada | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Czech Republic | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Denmark | 16 | 10 | 0 |
| France | 4 | 9 | 0 |
| Germany | 2947 | 818 | 51 |
| Greece | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Luxembourg | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Netherlands | 7 | 4 | 0 |
| Norway | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Poland | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Spain | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Sweden | 35 | 18 | 1 |
| Switzerland | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| United Kingdom | 3 | 4 | 0 |
| United States | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| Total | 2987 | 855 | 53 |
The investigation into the cause of the outbreak officially began with the notification of the Robert Koch Institute on 19 May concerning three cases of HUS in children in Hamburg.[26] On 26 May, German health officials hastily and prematurely announced that cucumbers from Spain were identified as a source of the E. coli outbreak in Germany,[27] when in fact the source were Egyptian sprouts. On 27 May 2011, German officials issued an alert distributed to nearby countries, identifying organic cucumbers from Spain and withdrawing them from the market.[14] The European Commission on 27 May said the two Spanish greenhouses suspected to be the sources had been closed, and were being investigated.[28][29] The investigation included analyzing soil and water samples from the greenhouses in question, located in the Andalusia region, with results expected by 1 June.[30] Cucumber samples from the Andalusian greenhouses did not show E. coli contamination,[31][32][33] but cross-contamination during transport in Germany and distribution in Hamburg are not discounted; in fact, the most probable cause is cross-contamination inside Germany.[34] The Robert Koch Institute advises against eating raw tomatoes, cucumbers, and lettuces in Germany to prevent further cases.[35]
On 31 May, an EU official said the transport chain was so long, the cucumbers from Spain could have been contaminated at any point along the transit route.[36] Spanish officials said before, there was no proof that the outbreak originated in Spain; Spanish Secretary of State for European Affairs Diego López Garrido said, "you can't attribute the origin of this sickness to Spain."[29]
On Tuesday 31 May, lab tests showed two of the four cucumbers examined did contain toxin-producing E. coli strains,[34] but not the O104 strain found in patients. The bacteria in the other two cucumbers have not yet been identified.[citation needed]
Genomic sequencing by BGI Shenzhen confirm a 2001 finding that the O104:H4 serotype has some enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC or EAggEC) properties, presumably acquired by horizontal gene transfer.[37][38][39]
The only previous documented case of EHEC O104:H4 was in South Korea in 2005, and researchers pointed at contaminated hamburgers as a possible cause.[40]
On 4 June, German and EU officials had allegedly been examining data that indicated an open catering event at a restaurant in Lübeck, Germany, was a possible starting point of the ongoing deadly E. coli outbreak in Europe.[41][42] German hospitals were nearly overwhelmed by the number of E. coli victims.[43]
A spokesman for the agriculture ministry in Lower Saxony, warned people on 5 June to stop eating local bean sprouts, as they had become the latest suspected cause of the E. coli outbreak.[44] A farm in Bienenbuettel, Lower Saxony, was announced as the probable source,[45][46] but on 6 June, officials said this could not be substantiated by tests. Of the 40 samples from the farm that were being examined, 23 had tested negative.[47] But on 10 June, the head of the Robert Koch Institute confirmed the sprouts were the source of the outbreak, and people who ate the sprouts were nine times more likely to have bloody diarrhea.[48][49] The WHO have confirmed on 10 June this statement on the update 13 of the EHEC outbreak.[50]
According to the head of the national E. coli lab at the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment, the strain responsible for the outbreak has been circulating in Germany for 10 years, and in humans not cattle. He said it is likely to have gotten into food via human feces.[51]
A joint risk-assessment by EFSA/ECDC, issued 29 June 2011, made a connection between the German outbreak and a HUS outbreak in the Bordeaux area of France, first reported on 24 June, in which infection with E. coli O104:H4 has been confirmed in several patients.[52] The assessment implicated fenugreek seeds imported from Egypt in 2009 and 2010, from which sprouts were grown, as a common source of both outbreaks, but cautioned, "there is still much uncertainty about whether this is truly the common cause of the infections", as tests on the seeds had not yet found any E. coli bacteria of the O104:H4 strain.[53][54] The potentially contaminated seeds were widely distributed in Europe.[55] Egypt, for its part, steadfastly denied it may have been the source of deadly E. coli strain, with the Minister of Agriculture calling speculations to that effect "sheer lies".[56]
Using epidemiological methods the outbreaks in 2011 were traced to a shipment of seeds from Egypt that arrived in Germany in December 2009.[5][8]
On 22 May, Health Commissioner John Dalli of the European Commission declared the issue to be an 'absolute priority', saying the commission is working with member states, particularly Germany, to identify the source of the outbreak.[57] Speaking again on 1 June, Commissioner Dalli noted the outbreaks have been limited in origin to the greater Hamburg area and declared any product ban would be disproportionate. He also said he is working with Agriculture Commissioner Dacian Cioloş "to address the hardship faced by this group of our citizens that has also been hit hard by the E. coli outbreak".[58] He also said, "In the future, we need to see how the timing of the alerts can be closer to the actual scientific basis and proof."[59]
By 7 June, EU Ministers held an emergency meeting in Luxembourg to discuss the growing crisis, which had left 23 people dead, and more than 2,000 ill so far.[59][60] Germany's Federal Agriculture Minister, Ilse Aigner, repeated her warnings to EU consumers to avoid eating any bean sprouts, cucumbers, tomatoes, and salads.[60]
The United States Center for Disease Control and the United States Department of Agriculture has long been concerned regarding risks involving the E. coli risk in raw bean sprout production.[59][failed verification]
Apart from the German government, which warned against the consumption of all raw cucumbers, tomatoes, and lettuce,[61] several countries implemented restrictions or bans on the import of produce.
Many other European countries took restrictive actions or lost sales of produce, including Albania, Croatia,[62] and Russia.
The ban on EU vegetables was lifted on 10 June, but stiff safety measures remained in place.[63]
Many countries took restrictive action. Egypt was a focus of the epidemiological investigation because the fenugreek seeds were imported into Germany from Egypt.[citation needed]
Egypt's Minister of Health Ashraf Hatem denied his nation had any patients infected with the new E. coli strain, due to the strict precautions brought in to test overseas tourists entering the country on 2 June.[64][65]
Responding to claims that Egyptian fenugreek seeds were the cause of the E. coli outbreak, Egyptian Minister of Agriculture Ayman Abu-Hadid told the Egyptian press the problem had nothing to do with Egypt and instead asserted, "Israel is waging a commercial war against Egyptian exports."[66]
Canada and the United States reported cases of E. coli infection that had been acquired in Europe.[citation needed]
On 2 June, Canada brought in stricter anti E. coli-related food inspections,[67] and by 3 June the Public Health Agency of Canada said no Canadians had been reported sick with the strain as of that date. The Canadian government also brought in heavier import and hygiene restrictions on EU cucumbers, lettuces, and tomatoes.[68]
The United States Department of Agriculture and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) stated that emerging strains of E. coli are a significant problem, but regulatory bodies in the US have concentrated on the more infamous E. coli O157 serotype.[69][70]
The FDA noted nearly all of America's fresh produce is grown in the US and areas of Central America, and the EU has not been a significant source of fresh produce for the US.[71]
Other countries, including Nigeria, Hong Kong, and Thailand, expressed concern regarding imported produce.[citation needed]
By 1 June, Italian, Austrian, and French cucumber sales had begun to decline sharply, but the Austrian Health Ministry official, Dr. Pamela Rendi-Wagner, claimed Austrian customers were still safe.[72]
On 3 June, the governments of Spain, Portugal, and Germany said they would formally request EU agricultural aid for farmers affected by the outbreak.[73] That day, Russia also set up plans for new imports of cucumbers from Ukraine, Azerbaijan, Egypt, and Turkey.[74][75]
By 7 June, the EU's farmers had reported they had lost millions of dollars in exports during the outbreak, with Fepex, Spain's fruit and vegetable industry group, saying its growers had $256,000,000 in turnover.[60] French, Swiss, Bulgarian, German, Dutch, Belgian, and Portuguese producers have also been similarly affected.[60]
That day, the EU proposed issuing £135,000,000 in agricultural compensation to its farmers. The EU agriculture commissioner said the EU's farmers could get back up to 30% of the cost of vegetables they were unable to sell.[76] The EU's health commissioner, John Dalli, had formally criticised Germany earlier that day for rushing out "premature conclusions" about the source of an outbreak, and only helped to spread alarm among the public and farmers and untimely leading to the damaging the EU's agriculture sector.[77] John Dalli also told the EU parliament in Strasbourg that claims had to be scientifically sound, unbiased, and fool-proof in nature before it was publicised in future.[78]
Spain then rejected the European Commission's €150,000,000/£135,000,000 compensation deal for their farmers who were hit by the E. coli outbreak, on 8 June, saying it was too small.[79] France, the European Union's largest agricultural grower, said it would support the plan to compensate producers hurt by the outbreak, according to the French Agriculture Minister Bruno Le Maire.[46]
Ministers from both EU and Russia were scheduled to meet on 8 June over Russia's earlier decision to ban all its vegetable imports from the EU.[80]
On 8 June, the EU's E. coli O104:H4 outbreak was estimated to have cost $2,840,000,000 in human losses (such as sick leave), regardless of material losses (such as dumped cucumbers).[81]
Consumers across Europe were shunning fruit and vegetables en masse by 8 June, as the German government's edict against eating raw cucumbers, tomatoes, lettuce and sprouts remained in place. EU farmers claimed to have losses up to C$417,000,000 a week as ripe vegetables rotted in their fields and warehouses.[82] On 8 June, The EU Farm Commissioner Dacian Cioloş said the EU had increased its offer of compensation to farmers for the losses caused by the E. coli outbreak to C$210,000,000.[82]
The outbreak was caused by a strain of E. coli of the serotype O104:H4, that was unusual for having characteristics of both enteroaggregative E. coli and enterohemorrhagic E. coli.[83] The strain has a number of virulence genes typical of enteroaggregative E. coli, including attA, aggR, aap, aggA, and aggC, in addition to the Shiga toxin variant 2.[26] All bacteria isolated from patients in this outbreak were resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics, third-generation cephalosporins, and partially resistant to nalidixic acid, but susceptible to carbapenems and ciprofloxacin.[26]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.