Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
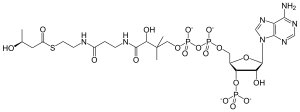
β-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA (or 3-hydroxybutyryl-coenzyme A) is an intermediate in the fermentation of butyric acid, and in the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan.[1][2] The L-3-hydroxybutyl-CoA (or (S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA) enantiomer is also the second to last intermediate in beta oxidation of even-numbered, straight chain, and saturated fatty acids.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-({[hydroxy({hydroxy[(3R)-3-hydroxy-3-({2-[(2-{[(3R)-3-hydroxybutanoyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]ethyl}carbamoyl)-2,2-dimethylpropoxy]phosphoryl}oxy)phosphoryl]oxy}methyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H42N7O18P3S | |
| Molar mass | 853.625 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.